- Is your horse sensitive to glyphosate?
- How does glyphosate kill plants?
- Is glyphosate toxic to animals?
- What are the effects of glyphosate on horses?
- Does glyphosate cause botulism in cattle?
- Why are horses so sensitive to ionophores?
- What happens if you give a horse too much glycoside?
- How long should horses be excluded from weed killer?
- What happens if you spray herbicide on horses?
- Will glyphosate kill marestail?
- Is glyphosate toxic to birds?
- Is glyophosate safe for horses?
- Is glyphosate harmful to horses?
- Does glyphosate affect ruminants?
- Why is glyphosate-based weed control important to animal agriculture?
- What is the prognosis of ionophore toxicity in horses?
- Are horses more sensitive to ionophores than other species?
- How to avoid ionic antibiotic toxicity in horses?
- What is botulinum toxin in cows?
- What bacteria causes botulism in cattle?
- Can horses get ionophores from cattle feed?
- How much alfalfa hay will kill a horse?
- Why is glyphosate more likely to bind Fe than CO2+?
- What causes botulism in feed?
- What are the main points on bovine botulism?
- What happens if a horse eats ionophores?
- What are ionophores in animal feed?
Is your horse sensitive to glyphosate?
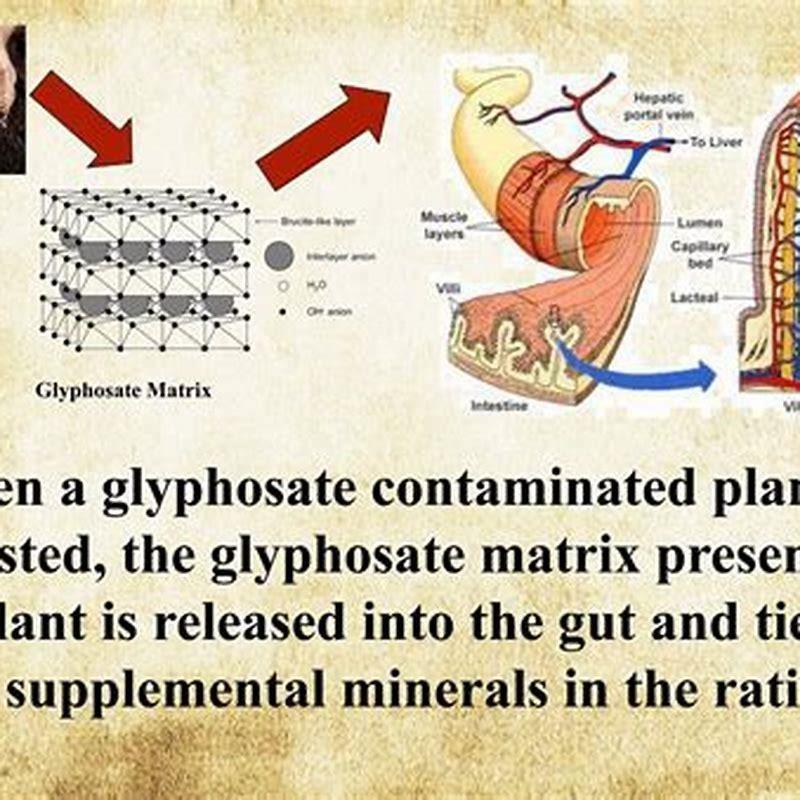
Last September, a vet-tech friend of mine in Texas, Lizzy Meyer, alerted me to the fact that her horse, Elto, had developed what she suspected was a glyphosate sensitivity. Glyphosate is Monsanto’s herbicide with the trade name Roundup . Elto’s symptoms included itchiness, hot spots, and edema over the kidneys.
How does glyphosate kill plants?
Glyphosate kills plants by interfering with a biochemical pathway involved in the synthesis of amino acids called the shikimate pathway. This pathway is not found in humans; however, the pathway is found in bacteria, and bacteria are critical to the GI tract to synthesize the essential amino acids.
Is glyphosate toxic to animals?
The tests also showed that glyphosate was poorly digested by mammals and was excreted largely unchanged. The report states that glyphosate is mildly toxic to wild birds but nontoxic to fish.
What are the effects of glyphosate on horses?
Given the scientific data and arguments, the possible effect of glyphosate on horses could be summarized as impaired homeostasis and metabolic function leading to chronic disease, loss of performance and even premature death.
Does glyphosate cause botulism in cattle?
A similar study on cattle found that glyphosate was toxic to beneficial bacteria in the GI tract and that glyphosate residues in cattle feed may predispose cattle to infection by Clostridium botulinum, the bacteria that causes botulism. What do we do now?
Why are horses so sensitive to ionophores?
Danger to horses Horses are more sensitive than other livestock to ionophores, which influence ion transfer across cell membranes and, thus, affect how nerves and muscles function.
What happens if you give a horse too much glycoside?
Danger to horses Potent cardiac glycosides in the plant affect the heart’s ion balance, causing irregular heart activity that can ultimately result in cardiac failure and death. Relatively small quantities (0.005% of the horse’s body weight, or 0.05 pounds for a 1,000-pound horse) are considered lethal. Ingestion might also cause colic.
How long should horses be excluded from weed killer?
Herbicide may make toxic weeds more palatable to horses. Horses should be excluded from the sprayed area for seven to ten days after treatment if poisonous plants are present. Herbicides alone will not result in a weed-free pasture.
What happens if you spray herbicide on horses?
Danger to horses Horses might be inclined to consume toxic plants they normally wouldn’t eat after they have been sprayed with herbicide, says Safdar Khan, DVM, MS, PhD, Dipl. ABVT, who previously served as director of toxicology at the ASPCA Animal Poison Control Center.
Will glyphosate kill marestail?
Correct and regular treatment with glyphosate weed killer will eventually kill the plant, more about that later. Marestail is an aquatic weed, Hippuris vulgaris, commonly found in ponds, slow flowing streams, bog land and even poorly drained domestic gardens.
Is glyphosate toxic to birds?
The report states that glyphosate is mildly toxic to wild birds but nontoxic to fish. Argentinean researchers reported that pregnant rats and their babies experienced abnormalities in their enzyme levels after the mother had been exposed to glyphosate, in research published in the March 2001 issue of “Environmental Research.”
Is glyophosate safe for horses?
Your horses will be fine, glyophosate or roundup is much better than any alternative weedkiller for safety. The idiot sales guys & agrics (I did a Crop Science Bsc) used to drink it and write their names in grass… still effective are going through a human!!
Is glyphosate harmful to horses?
Due to potentially higher levels present in the horse’s environment, Glyphosate could possibly be responsible for loss of performance and disease in horses. Such as laminitis, PPID, metabolic syndrome/IR, navicular syndrome, gastric ulcers, leaky gut syndrome and other immune conditions.
Does glyphosate affect ruminants?
For example, according to EFSA, the major contributor of glyphosate exposure for ruminants is grass (non-GE). Pastures can be treated with glyphosate for weed control at either preplant, pre-emergence, or postemergence for renovation or spot treatment.
Why is glyphosate-based weed control important to animal agriculture?
Glyphosate-based weed control is a critical tool to growers and the impact of yield losses is also important to animal agriculture because feed costs are the greatest expense to animal production systems.
What is the prognosis of ionophore toxicity in horses?
Supportive care such as intravenous fluids and pain relief is given to surviving animals. Vitamin E and selenium may help to offset muscle damage. The overall prognosis for ionophore toxicity in horses is poor to grave.
Are horses more sensitive to ionophores than other species?
Horses are much more susceptible to ionophore toxicity than are other species. For example, horses are nearly 20 times more sensitive than cattle and 200 times more sensitive than poultry to monensin toxicity, on a mg monensin per kg of body weight basis.
How to avoid ionic antibiotic toxicity in horses?
Prevention is the most effective way to avoid ionophore toxicity. Be sure to keep all feed that contains ionophore antibiotics away from your horse and away from your horse’s feed. Be sure to check on all horse feed recalls to ensure that your horse’s feed has not been recalled.
What is botulinum toxin in cows?
Botulinum toxin. Clostridium botulinum is commonly found in soil, water and marine sediments around the world, but it is also a normal inhabitant of the intestinal tract of many healthy horses, cattle and poultry. Other Clostridial bacteria cause diseases in farm animals including blackleg, black disease, swelled head, tetanus and enterotoxaemia.
What bacteria causes botulism in cattle?
A bacteria, Clostridium botulinum, causes botulism in cattle. The organism is a spore-forming, anaerobic, gram-positive rod, mainly proliferating in decaying animals and plant materials commonly reside in soil samples and aquatic sediments.
Can horses get ionophores from cattle feed?
Risk of exposure Horse feed can become contaminated with ionophores if manufacturers producing a variety of feed types don’t follow proper cleaning protocols between formulating batches for different species. “Exposure to cattle feed with the approved amount of ionophore is rarely a cause of intoxication in horses,” says Gaskill.
How much alfalfa hay will kill a horse?
If a horse ingests a lethal quantity (believed to be 0.5-1 mg of cantharidin per kilogram of body weight), he can die within 72 hours. Risk of exposure Alfalfa hay can become contaminated with beetles that are crushed during the crimping process (when hay stems are broken to hasten drying).
Why is glyphosate more likely to bind Fe than CO2+?
Furthermore, glyphosate is more likely to bind Fe than Co 2+ because the formation constant for glyphosate and Fe 2+ is similar to that of Co 2+, and that with Fe 3+ is significantly higher. The mode of action for the herbicidal effect of glyphosate is through EPSP synthase.
What causes botulism in feed?
Contaminated feed — contamination of feed rolls by carrion carcasses can result in large outbreaks on dairy farms, feedlots and intensive beef farms in a short time due to ingestions of feed containing the botulism toxin. Spoiled feed — decaying feed may contain botulinum toxin.
What are the main points on bovine botulism?
In my article, I shall discuss the main points on bovine botulism and ist prevention, treatment, and control. A bacteria, Clostridium botulinum, causes botulism in cattle. The organism is a spore-forming, anaerobic, gram-positive rod, mainly proliferating in decaying animals and plant materials commonly reside in soil samples and aquatic sediments.
What happens if a horse eats ionophores?
The doses of ionophores normally used in feed for other animals can be highly toxic to horses. Cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, and the neurologic system are affected by ionophore toxicity. Changes in movement of ions across cell membranes can kill cells, and muscle cells are very susceptible to the toxic effects of ionophores.
What are ionophores in animal feed?
Ionophore antibiotics are added to ruminant, swine and poultry feed to improve weight gain and control coccidiosis. There are several different ionophores that are approved for use in certain animal feed in the United States. Vet bills can sneak up on you. Plan ahead. Get the pawfect insurance plan for your pup. Protect yourself and your pet.