- What is the use of horse serum in humans?
- What is equine anti-tetanus toxoid serum?
- Is penicillin good for tetanus in horses?
- How long does tetanus toxoid last in horses?
- What are tetracycline antibiotics for horses?
- What is the best antibiotic for tetanus in horses?
- Are Clostridium tetani spores harmful to horses?
- How to treat toxoid toxicity in horses?
- How often do you give tetanus shots to horses?
- How deadly is tetanus in horses?
- Can humans get tetanus from horses in Ontario?
- What are antitoxins for horses?
- What causes tetanus in horses?
- What is penicillin used for in veterinary medicine?
- Can humans get CL tetani from horses?
- What is Clostridium tetani and what causes tetanus?
- What is the incubation period for herpes on a horse?
- What is the incubation period for Saw Horse Disease?
- What are the dangers of tetanus?
- How to euthanize a horse with tetanus?
- How to give a horse antibiotics?
- Can dogs and cats be given equine antitoxins?
- How dangerous is tetanus in horses?
- What causes tetany in horses?
- How is tetanus treated in a stallion with tetanus?
- What is tetanus and how does it affect horses?
What is the use of horse serum in humans?
Horse serum has been used in treatments against this disease in human patients. Equine anti-tetanus toxoid serum has been developed from horse serum as a vaccine against tetanus in human patients.
What is equine anti-tetanus toxoid serum?
Equine Anti-Tetanus Toxoid Serum Equine anti-tetanus toxoid serum has been developed from horse serum as a vaccine against tetanus in human patients. This serum has been used for years, but as it causes adverse effects in five to six percent of patients, scientists are looking for other treatments to replace it.
Is penicillin good for tetanus in horses?
Penicillin is the most commonly used antibiotic used to treat tetanus in horses. By the time symptoms become apparent, the neurotoxins produced by the bacteria have already bound to the nervous system. But antitoxins are still used to neutralize toxins in the bloodstream that have not yet caused nervous system damage.
How long does tetanus toxoid last in horses?
An intramuscular injection of 8-16 Lf tetanus toxoid in water-in-oil emulsion protected adult horses against tetanus for at least 128 weeks. A booster dose of 8 Lf toxoid in aqueous solution protected them for a further period of at least 3 1/2 years.
What are tetracycline antibiotics for horses?
Tetracycline antibiotics are a group of antibiotics that are effective against bacterial infections. Because they interfere with the normal growth cycle of the invading bacteria and prevent them from reproducing, the immune system of the horse is able to fight off the infection. Tetracyclines come in several forms.
What is the best antibiotic for tetanus in horses?
The veterinarian will begin antibiotics right away, both to treat the disease and to prevent further infection of the wound. Penicillin is the most commonly used antibiotic used to treat tetanus in horses.
Are Clostridium tetani spores harmful to horses?
Clostridium tetani organisms are present in the intestinal tract and feces of horses, other animals and humans, and are abundant as well as ubiquitous in soil. Spores of Cl. tetani survive in the environment for many years, resulting in an ever-present risk of exposure of horses and people on equine facilities.
How to treat toxoid toxicity in horses?
Whether or not the horse has been immunized, another injection of toxoid is usually given to increase the production of antibodies to the toxin. In the early stages of the disease, your veterinarian may recommend muscle relaxants, tranquilizers, or sedatives, in conjunction with tetanus antitoxin.
How often do you give tetanus shots to horses?
Adult non-vaccinated horses or horses with unknown status should receive an initial series of 2 doses of tetanus toxoid administered 3 to 6 weeks apart, followed by an annual booster.
How deadly is tetanus in horses?
Tetanus proves deadly in 50-75% of cases, so ensure your horse is adequately vaccinated. It’s a scenario that’s terrifying to imagine: Your horse’s muscles are contracting in spasms, he’s arching his back, and his body is rigid.
Can humans get tetanus from horses in Ontario?
Tetanus can also affect humans. The disease is not contagious between horses or between horses and humans. The number of horses affected with tetanus annually in Ontario is unknown but would appear to be low (less than 5). Cl. tetani is present in the feces and intestinal tracts of horses, and humans.
What are antitoxins for horses?
Antitoxins are products made of purified antiserum obtained from horses that have been immunized against tetanus. Antitoxin provides immediate passive (temporary) immunity similar to that a foal gains from the antibodies in colostrum, lasting only a few weeks.
What causes tetanus in horses?
Tetanus, one of the oldest recorded diseases of horses, is caused by the bacterium Clostridium tetani. Clostridium tetani is an anaerobic bacterium that is widespread in soil and can be carried in the intestinal tracts of many species.
What is penicillin used for in veterinary medicine?
Penicillin is an antibiotic produced by a form of mold and used medically as a bactericidal to kill bacteria that causes diseases. Penicillin, in various forms, is one of the most commonly used antibiotics in veterinary medicine. Different groups of penicillin are effective against different types of bacteria.
Can humans get CL tetani from horses?
Cl. tetani is present in the feces and intestinal tracts of horses, and humans. Soil contaminated with horse feces commonly contains Cl. tetani spores. Therefore, humans working around horses and horse farms should seek immediate medical attention when injured, especially with penetrating wounds such as those caused by nails.
What is Clostridium tetani and what causes tetanus?
Clostridium tetani is an anaerobic, gram-positive, spore-forming bacillus that causes tetanus by producing a potent exotoxin that is intensely toxic to humans and animals when it is formed in tissues or when injected. The organism is found in soil and in the intestinal tracts of humans and other animals.
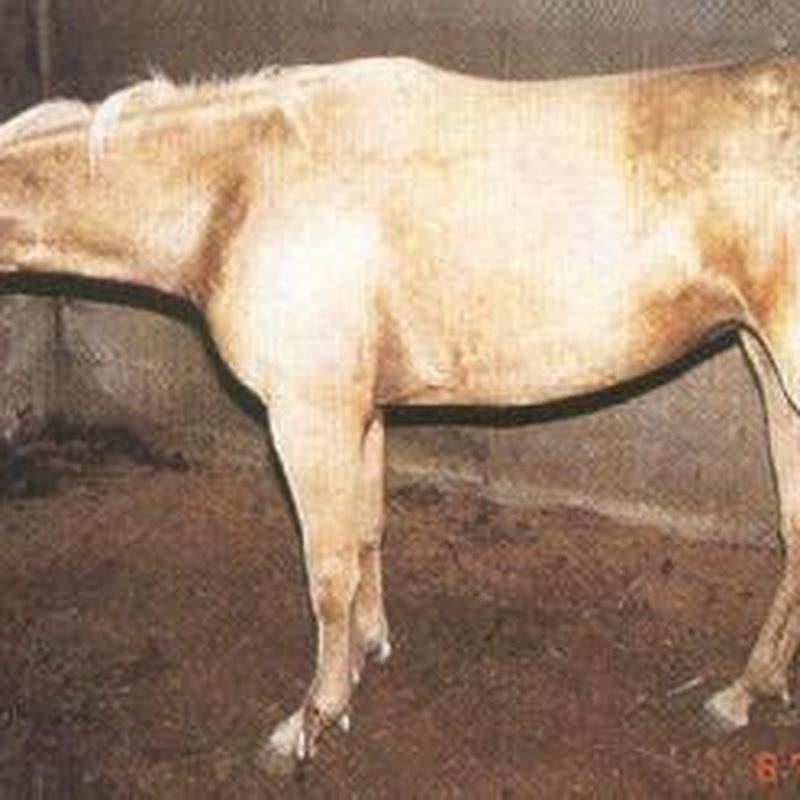
What is the incubation period for herpes on a horse?
Horses often adopt a “saw horse” posture. The incubation period is approximately 8 days (range 3 to 21 days) (1). Spores can also remain dormant in muscles and begin to grow when trauma occurs, making tissue oxygen level low.
What is the incubation period for Saw Horse Disease?
Horses often adopt a “saw horse” posture. The incubation period is approximately 8 days (range 3 to 21 days) (1). Spores can also remain dormant in muscles and begin to grow when trauma occurs, making tissue oxygen level low. Horses of all ages can be affected. Horses are the most susceptible of all of the animal species.
What are the dangers of tetanus?
The biggest danger is a deep, festering wound with dead tissue and pus, which is not exposed to fresh air. Horses and ponies are the most susceptible domestic animal to tetanus. They are readily exposed to the spores while grazing and their predilection for wounds such as lacerations and punctures make them prime candidates for acquiring tetanus.
How to euthanize a horse with tetanus?
Once the horse has collapsed, the most humane course of action is euthanasia. If a case is diagnosed early, however, large doses of tetanus antitoxin can be administered along with antibiotics, sedatives and muscle relaxants. Yet despite intensive treatment, most unprotected horses do not survive.
How to give a horse antibiotics?
ADMINISTRATION AND DOSAGE: Horses, inject one 1 mL dose intramuscularly using aseptic technique. Administer a second 1 mL dose 4 to 8 weeks after the first dose. Revaccinate annually using one 1 mL dose.
Can dogs and cats be given equine antitoxins?
The same approach as described for horses is used in treatment of dogs and cats, except that caution must be exercised in the intravenous administration of antitoxin, because the equine antitoxin may induce anaphylaxis. In one study, antitoxin was given to dogs with tetanus only after an intradermal test to detect hypersensitivity reactions.
How dangerous is tetanus in horses?
Perhaps surprisingly, a large, cleanish cut is a lower tetanus risk than a small puncture wound. The biggest danger is a deep, festering wound with dead tissue and pus, which is not exposed to fresh air. Horses and ponies are the most susceptible domestic animal to tetanus.
What causes tetany in horses?
Causes of Grass Tetany in Horses. Changes to grass make up in frosts/freezes. Early spring, lush grass may be too rich in protein. Autumn to early winter may see elevation of nitrate and potassium in the grass. Drought breaking rains. Stress from transport; the horse does not consume enough food.
How is tetanus treated in a stallion with tetanus?
The stallion was treated following tetanus management protocols indicated in Constable et al., 2017, i.e. to halt producedfurther propagation of the agent, neutralize the circulating toxins, control of muscle spasm.
What is tetanus and how does it affect horses?
Tetanus usually causes death in horses by asphyxiation when their diaphragm finally spasms. Everyone in the equine community should be aware of the dangers of tetanus for several reasons.