- What is the subject of the painting the small horse?
- How were horses used in the Mughal Empire?
- Why are Mughal paintings called Rajputs?
- How were horses used in pre-colonial India?
- Why is Mughal art so special?
- Why were horses so popular in the 16th century?
- Why is horse art considered second class art?
- How did the Mughal Empire ride their horses?
- Did the Mughal Empire have any illustrated books?
- What are the characteristics of Mughal art?
- Are there any paintings of animals and humans in Islamic art?
- Did the Mughals use semi-precious stones?
- What are the popular themes of Rajput paintings in India?
- Why Rajput’s were defeated by the Turko-Afghans and Mughals’?
- Which of the following paintings show strong Mughal influence?
- Why did artists paint battle scenes with large numbers of horses?
- What are some examples of prehistoric animals in art?
- How did horse racing influence the art of painting?
- Are there any medieval texts on horse riding techniques?
- What was the army of the Mughal Empire?
- What are the characteristics of Mughal architecture?
- What kind of paintings have been painted in the Mughal school?
- What was the Mughal Empire?
- What kind of weapons did the Mughal Empire use?
- Why did the Mughal Empire trade diamonds?
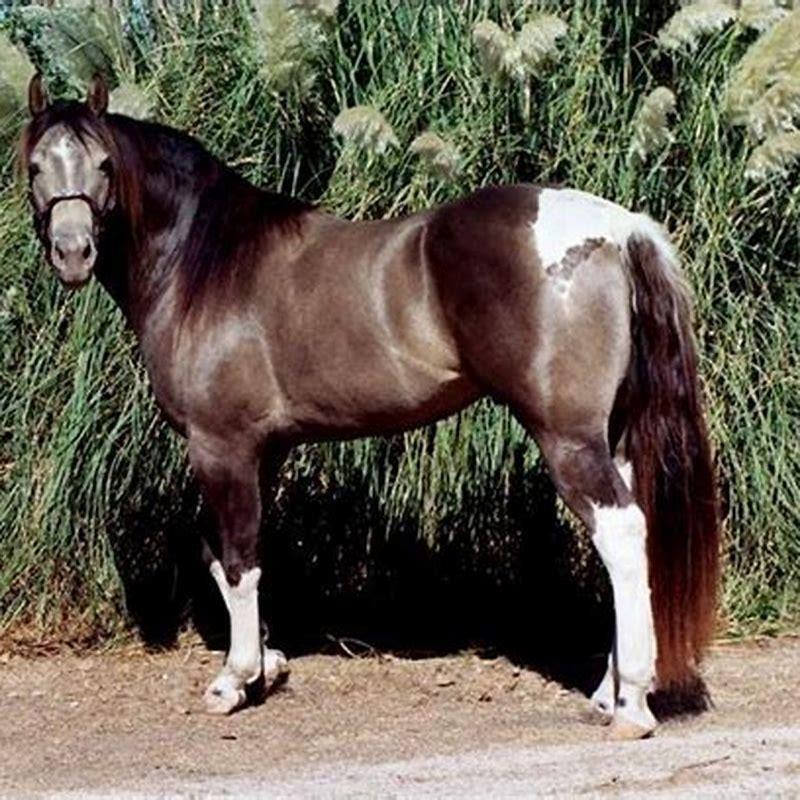
What is the subject of the painting the small horse?
Although he completed an entire series of etchings on horses, The Small Horse is particularly notable in that instead of an athletic show of grandiosity and freedom, the subject is restrained. This effect is emphasized by the tight and symmetrical composition and the sword which perspective-wise seems to be skewering the little horse in place.
How were horses used in the Mughal Empire?
In pre-colonial India, horses were used in wars, hunts and rituals. Horses were also the symbol of a ruler’s prestige. The mansabdar system during the Mughal rule – primarily under Akbar –institutionalised the use of horses.
Why are Mughal paintings called Rajputs?
They were free to make everything, and that’s why creativity of the Mughal Artists always shined. The Hindu painting is referred to as Rajput, as it is connected with Rajputana and the Hill Rajput of the Punjab; whilst the Islamic art is referred to as Mughal, as it owed its existence to the support it had from that dynasty.
How were horses used in pre-colonial India?
In pre-colonial India, horses were used in wars, hunts and rituals. Horses were also the symbol of a ruler’s prestige. The mansabdar system during the Mughal rule – primarily under Akbar –institutionalised the use of horses. Rajput nobles would be given military positions according to the number of horses they had in their cavalry.
Why is Mughal art so special?
Mughal Art is different. The Mughas used pretty basic tools in their artworks, and created breathtaking, finely painted art. Mughal Art flourished during the late 16th and 17th centuries with spectacular works by some of the best painters of that century like Miskin, Dana, and Daswan Baswanth
Why were horses so popular in the 16th century?
Whether for sport and entertainment, farm work, battle purposes, travel, or everyday pleasure riding, horses grew in popularity and necessity throughout the 16th century, and were clearly valued (maybe even loved) by many Tudor horse owners.
Why is horse art considered second class art?
In the Eighteenth century, the depiction of horses flourished, yet it was also considered second class art since horses were seen as humble objects rather than elevated objects. Horse-artists were referred to as animal painters and their talents were not fully recognized.
How did the Mughal Empire ride their horses?
Mughal horseman rides his horse confidently through the green countryside, raising his right arm backwards to let loose the falcon sitting on his wrist, Mughal, c. 1660. Johnson Album 67, 2. As featured in the British Library exhibition, Mughal India: A horse with elaborate saddle and harness being led by a groom.
Did the Mughal Empire have any illustrated books?
The largest commissions of illustrated books were usually classics of Persian poetry such as the epic Shahnameh, although the Mughals and Ottomans both produced lavish manuscripts of more recent history with the autobiographies of the Mughal emperors, and more purely military chronicles of Turkish conquests.
What are the characteristics of Mughal art?
Realistic portraiture, and images of animals and plants, was developed in Mughal art beyond what the Persians had so far achieved, and the size of miniatures increased, sometimes onto canvas.
Are there any paintings of animals and humans in Islamic art?
However, this rule has been interpreted in different ways by different scholars and in different historical periods, and there are examples of paintings of both animals and humans in Mughal, Persian, and Turkish art. Siyah Qalam (Black Pen), frequently depicts demonic creatures ( div) from Islamic narratives, but seem of Central Asian origin.
Did the Mughals use semi-precious stones?
From later periods, especially the hugely wealthy Ottoman and Mughal courts, there are a considerable number of lavish objects carved in semi-precious stones, with little surface decoration, but inset with jewels. Such objects may have been made in earlier periods, but few have survived.
What are the popular themes of Rajput paintings in India?
The 18th and early 19th century saw Rajput paintings illustrating episodes from the life of Krishna. The other popular themes of the 19th century were Ragamala and devotional subjects. Rajasthani paintings of Bikaner were also based on Mughal tradition.
Why Rajput’s were defeated by the Turko-Afghans and Mughals’?
Why Rajput’s were defeated by the Turko- Afghans and Mughals’? Rajput’s were defeated by the Turko- Afghans and Mughals’ due to the following reasons. The success of turko, Afghans and Mughals was the consumption of a process which extended till the establishment of Mughal Empire rather than the inferior cavalry of the Rajputs.
Which of the following paintings show strong Mughal influence?
Rajasthani Paintings show strong Mughal influence. Rajput painting originated in the royal states of Rajasthan, somewhere around the late 16th and early 17th century. The Mughals ruled almost all the princely states of Rajasthan at that time and because of this; most of the schools of Rajput Painting in India reflect strong Mughal influence.
Why did artists paint battle scenes with large numbers of horses?
However artists painting battle scenes with large numbers of horses and men, enabled the portrayal of action, of movement. Leonarado’s unfortunately lost painting, Battle of Anghiari, shows from drawings that survived, a consummate composition of life like actions and violence both of the horse and of man in extreme conditions.
What are some examples of prehistoric animals in art?
All the classic prehistoric animals are pictorialized here in a swirl of major works of art: the Great Black Bull, the three Chinese Horses, The Falling Cow, the Fleeing Horse, as well as more aurochs, more bulls, bison, ibexes, and horses.
How did horse racing influence the art of painting?
The sports of horse racing and fox hunting created a demand that artists scrambled to fill. Patrons were looking for accurate portraits of their prized horses. John Wootton (late 1600’s to mid 1700’s), James Seymour (1702-1752) were two painters who were quick to follow the new trend.
Are there any medieval texts on horse riding techniques?
In medieval times, we do not find texts which deal specifically with riding techniques.
What was the army of the Mughal Empire?
The Army of the Mughal Empire was the force by which the Mughal emperors established their empire in the 15th century and expanded it to its greatest extent at the beginning of the 18th century.
What are the characteristics of Mughal architecture?
Mughal architecture is the type of Indo-Islamic architecture developed by the Mughals in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries throughout the ever-changing extent of their empire in the Indian subcontinent. It developed the styles of earlier Muslim dynasties in India as an amalgam of Islamic, Persian, Turkic and Indian architecture.
What kind of paintings have been painted in the Mughal school?
We find, typical atmosphere of royalty even in the gathering for pleasure., Mostly historical scenes have been painted in Mughal School. Maximum, painting of historical scenes was done in Akbar’s time, because he gave much importance to, the manuscripts paintings such as, etc.,
What was the Mughal Empire?
The Mughal empire was one of the largest centralised states in pre-modern world history. It was founded in the early 1500s and by the end of the following century the Mughal emperor ruled almost the entire Indian subcontinent with a population of between 100 and 150 millions.
What kind of weapons did the Mughal Empire use?
During its conquests throughout the centuries, the military of the Mughal Empire used a variety of weapons including swords, bows and arrows, horses, camels, elephants, some of the world’s largest cannons, muskets and flintlock blunderbusses.
Why did the Mughal Empire trade diamonds?
Because of the Mughals’ insatiable desire for gems, precious metals, and decorative arts, the trade route from Goa to Agra became well established. An equally insatiable appetite for diamonds from the Golconda mines drove explorers and merchants to India, helping establish trade.