- Does a horse’s Withers rise up?
- What is the shape of a horse’s Withers?
- What is the difference between the withers and the stifles?
- What kind of saddle for a mutton withered horse?
- Why won’t my horse engage his back?
- Why do some saddles have higher withers?
- What happens if you saddle a horse wrong?
- What’s the best saddle for a mutton-withered horse?
- Why do horses withers change so quickly?
- Is your horse’s saddle causing pain?
- How do you know if a saddle is bad for You?
- What are the withers of the horse considered in evaluating conformation?
- What is the difference between Quarter Horse and regular horse bars?
- What is a full quarter horse called?
- How does a horse’s shoulder move?
- Do you need a saddle expert to check your fit?
- Why can’t my horse fit into this saddle?
- Does a horse’s standing conformation affect its performance?
- What causes Fistulous withers in horses?
- Why does my horse have Withers on his back?
- What is supraspinatus bursitis in horses?
- What is a recto-vaginal fistula in horses?
- What causes forging in horses?
- How to get rid of a fistula in a horse?
- How many horses are treated for Fistulous withers in New York?
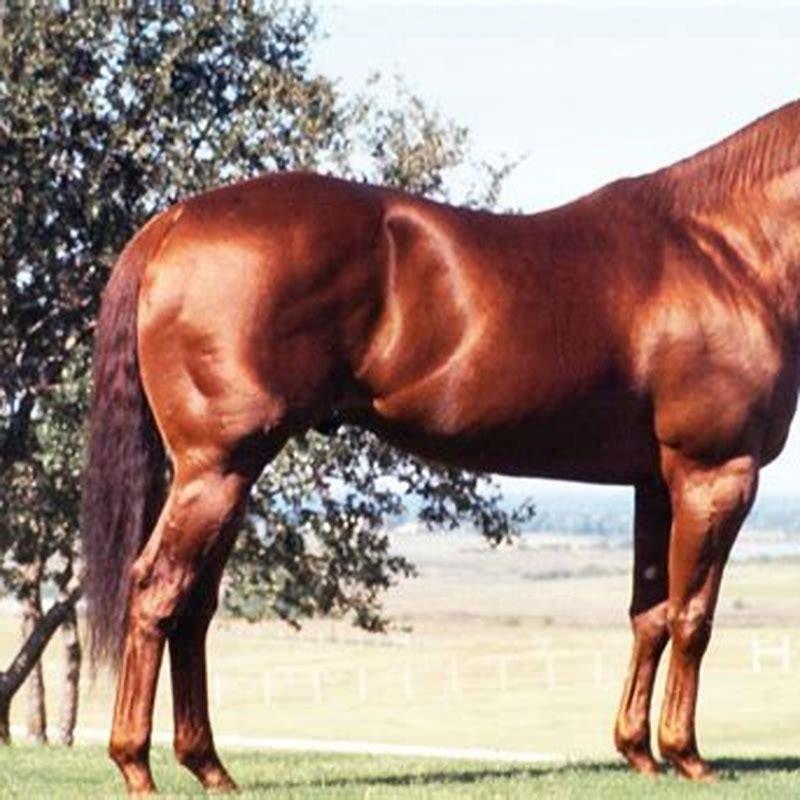
- What is the function of the withers on a horse?
Does a horse’s Withers rise up?
Yet in some horses, this bony ridge will be longer, while others are shorter. Nevertheless, it is the individual conformation differences in the neck, back, and shoulder areas of each horse that gives rise–or possibly no rise–to the shape of his withers.
What is the shape of a horse’s Withers?
However, the shape of a horse’s withers with regard to saddle fit is complex. “Your average horse’s withers will involve the fourth through 10th thoracic vertebrae,” says Joyce Harman, DVM, MRCVS. Yet in some horses, this bony ridge will be longer, while others are shorter.
What is the difference between the withers and the stifles?
either side of the withers is sunken vertebrae are higher than the surrounding muscle the hip bones are pointy and the muscle surrounding them sunken the width of the stifles is much narrower than the width of the hips
What kind of saddle for a mutton withered horse?
Here are more saddles that usually fit on a mutton withered horse that fit into a normal or narrow gullet: Take a look at the Billy Cook Trail Saddles or Tucker wide tree saddles. Another saddle that fits well is a Crates saddle with the equi-fit tree.
Why won’t my horse engage his back?
If you’re like Doris, you may be surprised to find that the most common culprit preventing a horse from engaging his back properly isn’t poor conformation or lack of pedigree but improper riding.
Why do some saddles have higher withers?
Higher haunches, or the horse built “downhill”, can allow the saddle to put more pressure on the withers and may require a pad that is built up in the wither area. A swayback causes “bridging” of the saddle.
What happens if you saddle a horse wrong?
Saddling a horse incorrectly not only influences your own riding technique but it can also be dangerous for both you and your horse. There are several different factors that affect the fit of a western saddle. Here is an outline of the major points on how to saddle a horse and how to avoid common mistakes.
What’s the best saddle for a mutton-withered horse?
The problem that mutton withers create in saddle fitting is that most saddles are built with normal withers in mind. The withers help keep the saddle in place, creating a ridge. The first thing we’d recommend for a mutton-withered horse is a saddle specially designed for your horse’s conformation. We have a few options.
Why do horses withers change so quickly?
Changes in the character of the withers can develop rapidly, too. Horses that are put into serious competition or work might start out heavier and wider while they are out of condition, but by mid-season they will have lost some fat in the topline and added muscle in t Create a free account with TheHorse.com to view this content.
Is your horse’s saddle causing pain?
Many horses will let you know if a poorly fitting saddle is causing them pain. If your equine friend exhibits unusual behavioral issues under saddle, have a saddle fitter out to see if the saddle might be causing discomfort. Sharing is caring!
How do you know if a saddle is bad for You?
However, the following are signs that the saddle you re riding isn t a good fit for you: Feeling insecure in the saddle. Feeling off balance or off center, like you re going to fall out. Difficulty keeping your alignment between hips and shoulders. Knee pain.
What are the withers of the horse considered in evaluating conformation?
The withers of the horse are considered in evaluating conformation. Generally, a horse should have well-defined withers, as they are considered an important attachment point for the muscles of the torso.
What is the difference between Quarter Horse and regular horse bars?
And while within one tree maker, the progression from Regular to Semi-Quarter Horse to Quarter Horse to Full Quarter Horse still goes from narrowest to widest, it doesn’t necessarily mean it is the same between makers. One maker’s Semi-Quarter Horse bars could be wider in spread and/or angle than another maker’s Quarter Horse bars.
What is a full quarter horse called?
Full-QH: Full Quarter Horse or FQHB can be referred to as Wide (usually 7” gullet). The angle is flatter compared to the Semi-QH tree.
How does a horse’s shoulder move?
The shoulder rotates freely backward, using the muscles attached to the withers. If the vertebrae of the withers are long, the shoulders have more room to rotate and the stride of the horse is long. This is very important for speed or jumping horses.
Do you need a saddle expert to check your fit?
So if you are an inexperienced rider, you may need a veteran to check your saddle fit for you; your discomfort might have to do with your riding, not the saddle. However, the following are signs that the saddle you’re riding isn’t a good fit for you: Our saddle experts are ready and willing to help with saddle fit problems.
Why can’t my horse fit into this saddle?
The more you ride the saddle, the more the tree is slowly disintegrating into a powdery mess. Because these companies are creating such generic trees, 50 to 60% of horses can’t even fit into them. The measurements are so generic that you’re lucky if it fits when it arrives.
Does a horse’s standing conformation affect its performance?
A horse’s standing conformation may not have much to do with it’s performance ability. There is often more to performance success than conformation. A horse must be fit and in good condition, with a sound mind and body. The horse’s willingness and ‘heart’ attitude may overcome a conformation flaw.
What causes Fistulous withers in horses?
Actinomyces bovis and Brucella abortus are the common organisms responsible for fistulous withers, blunt trauma to the withers caused by tack or sharp contact with a fence or another horse or object can lead to infection and inflammation resulting in fistulous withers.
Why does my horse have Withers on his back?
Blunt trauma to the withers and infection of an open wound may also lead to the inflammation resulting in fistulous withers. Trauma may be caused by an ill fitting saddle or harness, but may also be caused by sharp contact with a fence, another horse, or from a gun shot wound.
What is supraspinatus bursitis in horses?
Supraspinatus Bursitis. Septic supraspinous bursitis, commonly referred to as ‘fistulous withers’, is characterized by a profuse serofibrinous exudate with varying amounts of skin necrosis at the supraspinous bursa (the region of the horse’s withers and associated tissues) that turn into distended fistulous tracts.
What is a recto-vaginal fistula in horses?
When a recto-vaginal fistula occurs during the birthing process, it is usually due to a foot of the foal causing the tear. The fistula may also be a result of the manual manipulation that occurs when someone is helping the horse give birth and in some cases is the result of the mare’s efforts to deliver their foal.
What causes forging in horses?
Exhaustion, laziness, or an underlying condition can cause forging to occur, but more often it is a conformation problem. This results in the hind foot advancing too quickly, while the front leg is lifted too slowly.
How to get rid of a fistula in a horse?
The most common method of treatment is surgery to remove the tissue from the infected fistula. The veterinarian will recommend your horse to an equine surgery clinic or equine hospital. The surgery will be followed up by antibiotics to prevent any further infection.
How many horses are treated for Fistulous withers in New York?
Over an 8-year period, 14 horses were admitted to the New York State College of Veterinary Medicine for evaluation of fistulous withers. Of the 14 horses, 11 were treated surgically and 3 were not treated.
What is the function of the withers on a horse?
The withers act as a fulcrum, balancing the actions of the muscles and ligaments so that when the horse lowers and extends his neck, his back lifts—a mechanical action essential for collection. They also help determine his stride.