- Can you break a horse’s will?
- Is it cruel to break a horse?
- What does fear look like in a horse?
- How do Horses Act when they are scared?
- Why is it important to recognize when a horse is frightened?
- What age do you break a Connemara horse?
- Is ethology compatible with high-level education in horse breaking?
- What do your horse’s ears say about his mood?
- What is anaphylactic shock in horses?
- What happens when a horse is in shock?
- How can I help my horse with equine anxiety?
- What does it mean when a horse is frightened?
- What happens when a horse is scared or in pain?
- What makes a horse not useful?
- Can a horse teach us about learning theory?
- What is the main goal of managing behavior problems in horses?
- Are there any Connemara ponies that have made history?
- What is a Connemara/Thoroughbred?
- How can you tell if a horse is fearful?
- How do you know if your horse is scared?
- How can you tell if a horse is listening to you?
- What does a horse’s eye say about his mood?
- What causes osselets in horses?
- What is anaphylactic shock and what causes it?
- What causes allergic reactions in horses?
- What happens when a horse has anaphylactic shock?
Can you break a horse’s will?
But some trainers and riders have taken the word quite literally: breaking a horse of undesired habits, breaking his will to resist the confines and pressures of saddle and bridle … even breaking his spirit to flee perceived danger.
Is it cruel to break a horse?
Make sure you are safe at all times and that someone is with you if necessary who is more knowledgeable but don’t be afraid and take the lead.There is no excuse when horse breaking to be cruel, and remember animals including horses are not born bad, they react to what we as humans do to them.
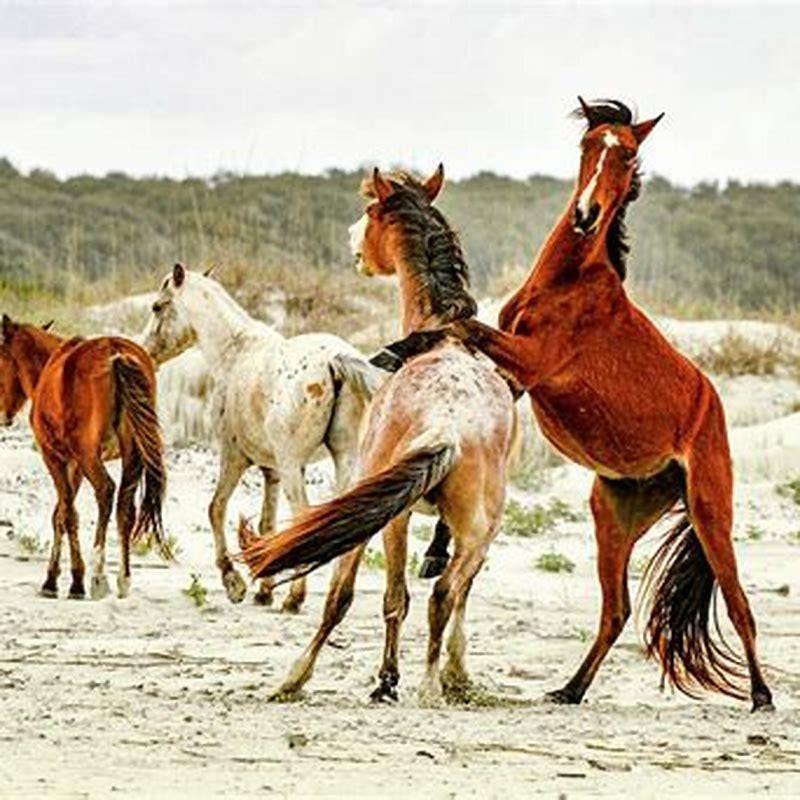
What does fear look like in a horse?
Depending on the situation, a horse’s expression of fear may look different. A horse that’s in a stall and scared of human reaction will stand at the other end of the stall and stay away while a horse that’s afraid of a certain object may prance about and bolt.
How do Horses Act when they are scared?
Typically when a horse is scared, they look and focus on the object, arch their neck and snort. The rapid exhalation of air is an audible clue to others in the herd to pay attention to the scary object. In a group situation, if one horse snorts the other horses will usually all look and pay attention to see if there is a threat.
Why is it important to recognize when a horse is frightened?
It is important for anyone who will be around horses to recognize when a horse is frightened for their own safety and that of the animal.
What age do you break a Connemara horse?
Depending on the future use of the horse, they will be broken in between 2.5 and 3.5 years old. For Sophie Bolze, breeder of Connemara ponies in the center of France, handling begins even before weaning:
Is ethology compatible with high-level education in horse breaking?
The Haras de Hus has chosen ethology as the prefered technique for breaking-in their horses. With the results, it is proof that high-level education and ethology are compatible (as if it was still to be proven…).
What do your horse’s ears say about his mood?
The position of a horse’s ears says a lot about his mood. If his ears are flicking back and forth, your horse is probably frightened or overly stimulated. He is flicking his ears around to pinpoint the source of his anxiety. If his ears are perked forward, he is alert and interested in his surroundings.
What is anaphylactic shock in horses?
(See Anaphylactic Shock below) If horse owners find their horse in a situation where there is severe blood loss, colic or trauma, they can suspect their horse is already in or may soon suffer shock.
What happens when a horse is in shock?
Deprived of oxygen and nutrients, the organs begin to fail. If the shock isn’t treated, the horse will eventually lose consciousness, the heart will stop and the horse will die. Horses suffer shock for a number of reasons including injury, colic, extreme fear, blood loss and dehydration.
How can I help my horse with equine anxiety?
The only way to deal with most things that cause equine anxiety is repetition, because they’re things you just can’t change or that your horse just has to deal with. | Photo Courtesy of EQUUS Remove The Cause? Once you’ve isolated the cause of your horse’s consternation, the big question is what can you do about it?
What does it mean when a horse is frightened?
The horse may be anxious or in pain. This frightened horse is leaning back with head raised and turned to face alarming object, ready to flee, ears held back, whites of eyes showing with tense muscles above, tense muzzle with square nostrils. The horse is about to run away. This horse is not happy and wants you to stay away or go away.
What happens when a horse is scared or in pain?
If a horse is scared or in pain, it will seek ways to escape the pressure it is feeling. It is extremely important to use the sense of touch to create a willing partnership between horse and human rather than a servitude based on fear. It is very important to understand how the horses eyes work.
What makes a horse not useful?
Except for breeding stock, horses are useful only when in motion. In a very real sense, the horse is an athlete. Any physical handicap that causes it to be clumsy, use excessive energy to perform a task, be hard riding, lack strength or speed, or wear excessively, decreases its potential usefulness.
Can a horse teach us about learning theory?
A regular feature of this review concerns the observation that learning theory has mostly been developed from experiments on laboratory animals, notably rats and pigeons. Observation of the ridden horse provides a window into the processes of negative reinforcement, and escape and avoidance learning within a practical context.
What is the main goal of managing behavior problems in horses?
The main goal of managing behavior problems in horses is to identify the deviation from normal equine behavior and correct it. Aggression is a common problem in horses and includes chasing, neck wrestling, kicks and bites, and other threats.
Are there any Connemara ponies that have made history?
7) Many Connemara ponies have made history. Little squire: Was known as the “Littest horse with the biggest heart” in the US. He won open championship by clearing fences that were 7 foot in height. The Nugget: won over 300 hundred international competitions.
What is a Connemara/Thoroughbred?
Another American Connemara/Thoroughbred, a 14.2hh grey gelding called Seldom Seen, competed against warmbloods in grand prix dressage in the late 1980s with rider Lendon Gray. Gray told Eurodressage: “This was the time that people started to flock to Europe to buy big fancy warmbloods.
How can you tell if a horse is fearful?
Fear can be identified by watching a horses behavior and looking for tell tale signs. We have to remember that horses are prey animals and it is there nature to be cautious and fearful. In the wild, the last horse to run may be the first one to get eaten by a predator.
How do you know if your horse is scared?
If you notice your horse being skittish about something particular, that’s when you know that you have to do something about it. If you start avoiding certain areas or certain objects with your horse, your horse is actually going to get more scared.
How can you tell if a horse is listening to you?
1 Ears Back. Usually this means a horse is angry and is threatening another horse. … 2 One or Two Ears Slightly Back. This means the horse is listening to something behind him. … 3 Ears Forward. If the ears are held forward and the horse is attentive, it means the horse is listening. … 4 Tail Swishing. … 5 Bucking. … 6 Rearing.
What does a horse’s eye say about his mood?
The look in a horse’s eye is a very good indicator of his mood. It will also help you to interpret other body signals. Generally speaking a horse will have a bright open eye. I am only pretending to be ‘asleep’, but in reality I am getting ready to explode! You’re in trouble now! Kicks are not just for protection.
What causes osselets in horses?
Osselets in horses is caused by chronic stress injury to the fetlock joint to one or both legs. Chronic stress injury can happen by: Re-occurring shock forces during racing and training Hard training in young horses
What is anaphylactic shock and what causes it?
Anaphylactic shock is a rare, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction to an antigen (a foreign substance that stimulates the immune system). Insect stings, certain foods or medicines and vaccines can be culprits. When the body is exposed to the antigen, histamine and other chemicals are released into the bloodstream.
What causes allergic reactions in horses?
Many things can trigger allergic reactions, among them environmental allergens such as dust, pollen, and mold; insect bites; substances in feeds; things put on or touched by the horse; or injections. An allergy is a condition in which the body reacts adversely (locally or systemically) to a certain substance (allergen).
What happens when a horse has anaphylactic shock?
Anaphylactic reactions are usually quite sudden and severe. Blood pressure drops dramatically, and the respiratory system is compromised due to internal swelling, causing the horse to have trouble breathing. He might collapse and die unless the condition is immediately reversed with medications such as epinephrine.