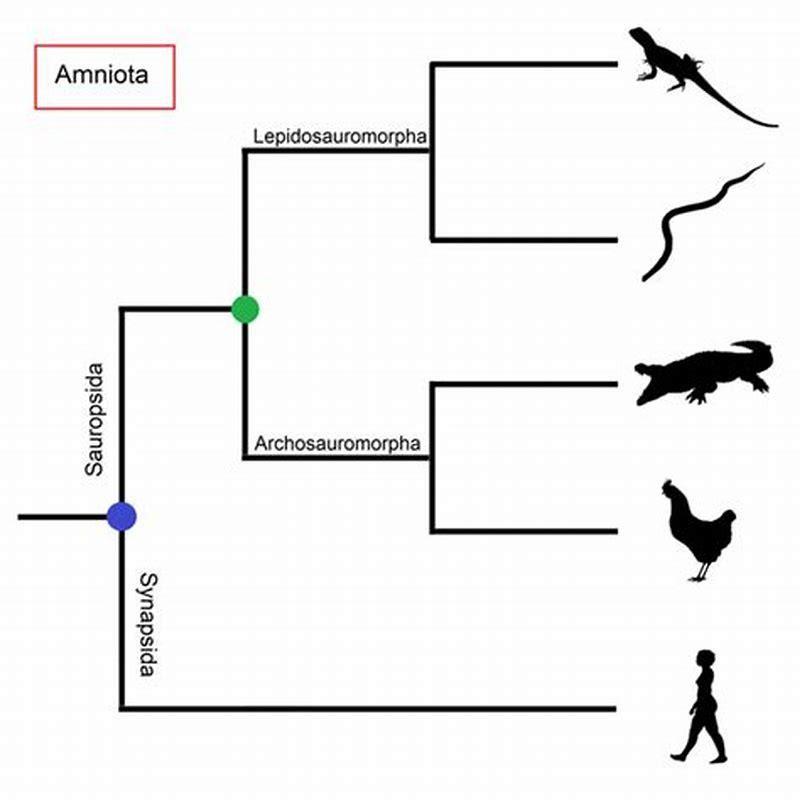
- Do reptiles have physical placodes?
- Do reptiles have placodes?
- Do lizards have placodes?
- What animals share the same placodes?
- How can you tell if something is inherited from a reptile?
- What are the homologous structures inherited from reptiles?
- What are placodes in reptiles?
- How do we recognize reptilians?
- What is an example of homology and homoplasy?
- What is homology in biology?
- What is the difference between homology and divergent evolution?
- What are homologous structures?
- Are humans reptilian in nature?
- What are the homologous structures of the hand and finger bones?
- Do homologous structures always have a common ancestor?
- What are homologous structures give examples?
- What are homologous organs?
- Can homologous structures be used as a measure of evolution?
- What is homoplasy in evolution?
- What are homologous structures in biology?
- Are the forelimbs of mammals analogous or homologous?
- What is the relationship between homology and evolution?
- Which of the following is an example of divergent evolution?
- What is the difference between speciation and divergent evolution?
- How does parallel evolution differ from divergent evolution?
Do reptiles have physical placodes?
They found that the amount of EDA present in cells correlated with size of scales. More EDA meant longer scales; no EDA, no scales. As the team studied the EDA gene, they discovered the solution to the evolutionary debate: Contrary to previous findings, reptiles do have physical placodes. “They were always there,” Milinkovitch said.
Do reptiles have placodes?
More EDA meant longer scales; no EDA, no scales. As the team studied the EDA gene, they discovered the solution to the evolutionary debate: Contrary to previous findings, reptiles do have physical placodes. “They were always there,” Milinkovitch said.
Do lizards have placodes?
“Now we are lucky enough to put this debate to rest, because we found the placodes in all reptiles: snakes, lizards and crocodiles.” In their paper, published in the journal Science Advances, Dr. Milinkovitch and his team report the first findings of the anatomical structures in Nile crocodiles, bearded dragon lizards and corn snakes.
What animals share the same placodes?
They concluded that birds, mammals and reptiles all inherited their placodes from the same ancient reptilian ancestor. The dark spots stained blue are placodes, which develop into scales, feathers and hair. The animals from left to right are a mouse, snake, chicken and crocodile.
How can you tell if something is inherited from a reptile?
Check the placode. A picture showing scales (in a corn snake). Mammalian hairs, avian feathers, and reptilian scales are homologous structures inherited, with modification, from their shared reptilian ancestor’s scales, according to a new study published Friday in Science Advances.
What are the homologous structures inherited from reptiles?
Mammalian hairs, avian feathers, and reptilian scales are homologous structures inherited, with modification, from their shared reptilian ancestor’s scales, according to a new study published Friday in Science Advances.
What are placodes in reptiles?
The dark spots stained blue are placodes, which develop into scales, feathers and hair. The animals from left to right are a mouse, snake, chicken and crocodile. Credit… Why did no one find placodes in reptiles before?
How do we recognize reptilians?
“So another question you’ve asked me, is how, or is there any tricks by which we can recognize those that which are in fact reptilians… they have a greenish, grey skin, they have scales in certain places over the body and very small ears, their eyes are somewhat larger than ours but the pupil has a little slit. The 4 hints I can give you, becaus…
What is an example of homology and homoplasy?
The wing of birds and bats is an example where both homology and homoplasy are present. The bones within the wings are homologous structures that are inherited from a common ancestor. All wings include a type of breastbone, a large upper arm bone, two forearm bones, and what would be hand bones.
What is homology in biology?
The term homology refers to biological structures or characteristics that are similar or the same. These characteristics are found on two or more different species when those characteristics can be traced to a common ancestor.
What is the difference between homology and divergent evolution?
A homoplasy evolves independently, usually due to natural selection in similar environments or filling the same type of niche as the other species which also have that trait. A common example often cited is the eye, which developed independently in many different species. Homology is a product of divergent evolution.
What are homologous structures?
Structures which do not have a common basic structure but perform different functions are called homologous structures. Structures which have a common basic structure but perform same functions are called homologous structures.
Are humans reptilian in nature?
Humans would be reptilian in nature and most of our world religions would have reptiles rather than giant humans such as seen in the Sumerian tablets of the humanoid Anunnaki.
What are the homologous structures of the hand and finger bones?
The hand bones are just one long thick bone, and the finger bones are just one long thick finger with a modified nail or hoof. In the whale flipper, the bones are very short and thick. Bat and bird wings, the front leg of a horse, the flipper of a whale, and the arm of a human are homologous structures.
Do homologous structures always have a common ancestor?
For example, forelimbs of reptiles, amphibians and mammals. Yes, homologous structures always have a common ancestor from which they have evolved along different directions due to adaptations to different needs. Is there an error in this question or solution?
What are homologous structures give examples?
Homologous structures are those structures which have a common basic structure but perform different functions. For example, forelimbs of reptiles, amphibians and mammals. Yes, homologous structures always have a common ancestor from which they have evolved along different directions due to adaptations to different needs.
What are homologous organs?
Homologous Organs are those organs of various animals that have similar basic structures but perform different functions. Homologous Organs provide evidence for the evolution of organisms.
Can homologous structures be used as a measure of evolution?
Homologous structures in modern organisms may show even less similarity in form, but it’s still possible to trace their development and use them as a measure of evolutionary relatedness.
What is homoplasy in evolution?
Homoplasy, on the other hand, is due to convergent evolution. Here, different species develop, rather than inherit, similar traits. This may happen because the species are living in similar environments, filling similar niches, or through the process of natural selection.
What are homologous structures in biology?
Homologous structures are structures that are derived from a common ancestor i. e. they have a common evolutionary ancestry. This is not to say that homologous structures have the same function e. g. a whale’s flipper is homologous to a human arm.
Are the forelimbs of mammals analogous or homologous?
Both originated in the forelimbs of early mammalian ancestors, but they have undergone different evolutionary modification to perform the radically different tasks of flying and swimming, respectively. Sometimes it is unclear whether similarities in structure in different organisms are analogous or homologous.
What is the relationship between homology and evolution?
Since homologues have to evolve in the first place, a connection to explanations of evolutionary novelties exists. Traditional morphology, including pre- evolutionary morphology and comparative embryology, was fundamentally concerned with understanding morphological organization.
Which of the following is an example of divergent evolution?
Mammals are an example of divergent evolution because they became very dissimilar over a long period of time, yet still retain similar structures that indicate they are related somewhere on the tree of life.
What is the difference between speciation and divergent evolution?
While it is a very fast type of speciation, divergent evolution generally takes more time.
How does parallel evolution differ from divergent evolution?
Parallel evolution differs from divergent evolution in that when parallel evolution occurs two already different species end up with similar traits while in divergent evolution one species (or very closely related species) evolves into two distinct species due to the development of different unique traits within the species itself over time.