- How does the respiratory system of birds work?
- Why do birds have such small lungs?
- How does gas exchange occur in the lungs?
- Where do the air sacs of birds extend into?
- How does the respiratory system of a bird work?
- How do birds breathe when they have no diaphragm?
- What is the function of the lungs in birds?
- Where does gas exchange occur in the avian respiratory system?
- Why is gas exchange in birds so efficient?
- What happens when a bird inhales and exhales?
- What is the structure of the respiratory system in birds?
- How does the respiratory system of birds differ from that of mammals?
- What is the respiratory cycle of a bird?
- How does the respiratory system of a bird communicate?
- What happens to the air in a bird’s lungs?
- How do birds breathe through their rib cage?
- Why do birds breathe differently from mammals?
- Do birds have a diaphragm?
- What is the function of air sacs in birds?
- How does oxygen diffuse through the air in the avian lung?
- Where does avian gas exchange occur?
- How does the avian respiratory system work?
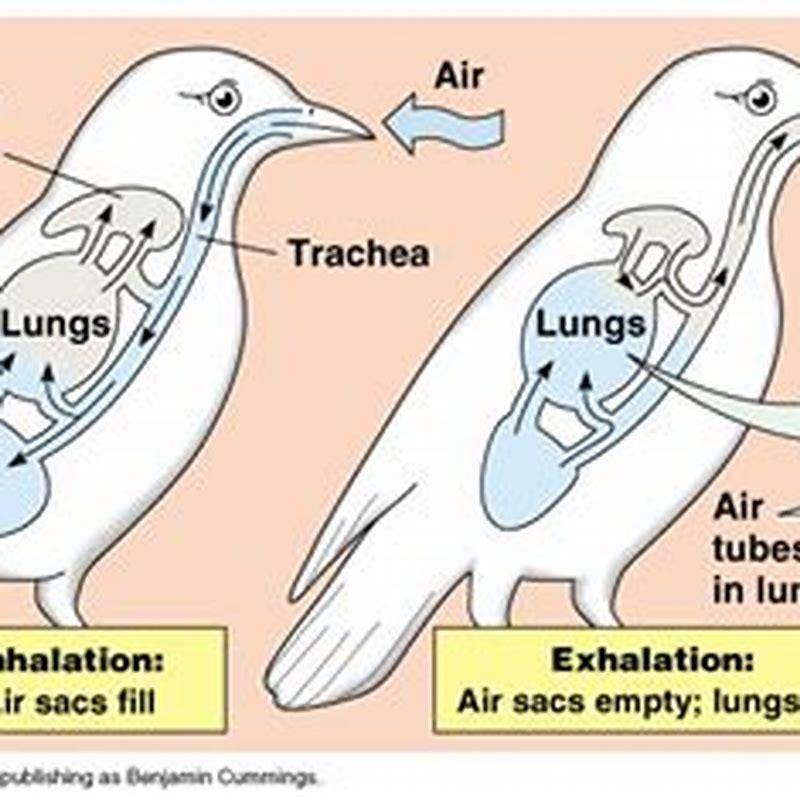
How does the respiratory system of birds work?
The respiratory system of birds facilitates efficient exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen by using air sacs to maintain a continuous unidirectional airflow through the lungs. The avian respiratory system is physically distinct from the mammalian respiratory system, both in structure and in its ability to exchange gas as efficiently as possible.
Why do birds have such small lungs?
But in birds these processes of gas exchange and ventilation happen in two different organs. They have relatively small lungs so that the organs needed for both gas exchange and ventilation can function in such a small space.
How does gas exchange occur in the lungs?
The inhaled air travels down each primary bronchus and then divides: some air enters the lungs where gas exchange occurs, while the remaining air fills the posterior (rear) air sacs. Then, during the first exhalation, the fresh air in the posterior sacs enters the lungs and undergoes gas exchange.
Where do the air sacs of birds extend into?
The air sacs of birds extend into the humerus (the bone between the shoulder and elbow), the femur (the thigh bone), the vertebrae and even the skull. So the correct answer is ‘Air sacs’.
How does the respiratory system of a bird work?
A finely tuned respiratory system that moves air in one direction enables birds’ high activity level. And the air sacs help regulate temperature by providing a mechanism to dissipate excess body heat.
How do birds breathe when they have no diaphragm?
Birds do not have a diaphragm, so air is displaced into and out of the respiratory system by changes in the pressure of the air sacs. The chest muscles cause the sternum to be pressed outward, creating a negative pressure in the sacs that allows air to enter the respiratory system (Maina J. N., 2005).
What is the function of the lungs in birds?
In the avian lung, oxygen diffuses (by simple diffusion) from the air capillaries into the blood & carbon dioxide from the blood into the air capillaries (shown in this figure and in figures below ). This exchange is very efficient in birds for a number of reasons.
Where does gas exchange occur in the avian respiratory system?
‘ In the avian lung, the gas exchange occurs in the walls of microscopic tubules, called ‘air capillaries. ‘ The respiratory system of birds is more efficient than that of mammals, transferring more oxygen with each breath.
Why is gas exchange in birds so efficient?
This exchange is very efficient in birds for a number of reasons. First, the complex arrangement of blood and air capillaries in the avian lung creates a substantial surface area through which gases can diffuse.
What happens when a bird inhales and exhales?
When the bird inhales, the lungs fill up as well as the air sacs. This allows the bird to take in more oxygen. When the bird exhales, the air from the lungs exits the body, but the air from the air sacs enters into the lungs. When the oxygen from the air sacs enters into the lungs, it is distributed to the body.
What is the structure of the respiratory system in birds?
The bird’s respiratory system consists of paired lungs, which contain static structures with surfaces for gas exchange, and connected air sacs, which expand and contract causing air to move through the static lungs.
How does the respiratory system of birds differ from that of mammals?
In mammalian lungs, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in microscopic sacs in the lungs, called ‘alveoli.’ In the avian lung, the gas exchange occurs in the walls of microscopic tubules, called ‘air capillaries.’. The respiratory system of birds is more efficient than that of mammals, transferring more oxygen with each breath.
What is the respiratory cycle of a bird?
Respiratory cycle of a bird During the first inspiration, the air travels through the nostrils, also called nares, of a bird, which are located at the junction between the top of the upper beak and the head. During the first expiration, the air is moved from the posterior air sacs through the ventrobronchi and dorsobronchi into the lungs.
How does the respiratory system of a bird communicate?
The respiratory system of birds is also used for communication through song. The “voice box” is the syrinx, a membranous structure at the lower end of the trachea. Sound is produced only when air flows outward across the syrinx.
What happens to the air in a bird’s lungs?
As air passes through the ductwork of the lungs, oxygen in the air is exchanged for carbon dioxide in the blood of capillaries winthin the chamber walls. The bird has two sets of air sacs. The caudal air sacs include the abdominal air sac and the caudal thoracic air sacs.
How do birds breathe through their rib cage?
Instead, birds use muscular contractions to move their rib cages, which pumps air through their bodies. Because of their elongated respiratory system, birds store the air in their bodies for two breathing cycles. When a bird inhales, the air it breathed in is not expelled the next time it exhales; instead,…
Why do birds breathe differently from mammals?
Birds breathe differently from mammals because they lack a diaphragm. They move air in and out of their lungs and air sacs by means of special muscles that move the ribs and sternum downward and forward, expanding the body cavity and causing inspiration, and then up and backward, contracting the body cavity and causing expiration.
Do birds have a diaphragm?
Extra care should be used when handling birds not to restrict the chest. Birds do not have a diaphragm and must use thoracic muscles to breathe. Compared to many other species, avian patients are easy to intubate. Most birds lack a glottis and visualization of the trachea is straightforward.
What is the function of air sacs in birds?
Air sacs have very thin walls with few blood vessels. So, they do not play a direct role in gas exchange. Rather, they act as a ‘bellows’ to ventilate the lungs (Powell 2000). Air sacs and axial pneumatization in an extant avian.
How does oxygen diffuse through the air in the avian lung?
In the avian lung, oxygen diffuses (by simple diffusion) from the ‘air capillaries’ into the blood & carbon dioxide from the blood into the ‘air capillaries’. Air (passing through the parabronchi) & blood (moving through capillaries) travel at right angles to each other.
Where does avian gas exchange occur?
Avian Gas Exchange. Avian Gas exchange takes place not in alveoli, as in mammals, but within air capillaries which are extensions of the parabronchial lumen. They are an interconnecting network of loops, and closely intertwine with blood capillaries. The air capillaries and blood capillaries are arranged so that flow is crosscurrent.
How does the avian respiratory system work?
The key to the avian respiratory system is that air moves in and out through distention and compression of the air sacs, not the lungs. The air sacs act as bellows to suck air in and blow it out and to hold part of the total air volume.