- What is an air sac in birds?
- Where does the air enter the lungs of a bird?
- What is the function of the anterior air sacs?
- Which animal has the most air sacs?
- What is the pulmonary system in birds?
- What are air sac mites in birds?
- What is an air sac and why is it important?
- What is the function of the air sacs in a bird?
- What is the respiratory system of a bird?
- Why do bird lungs have more oxygen than mammal lungs?
- What happens to the spent air in the anterior air sacs?
- What is the role of the respiratory system in birds?
- What is the function of air sacs in the lungs?
- Why do birds have air sacs in their lungs?
- How many air sacs does a bird have?
- What animal has the most air pockets in its bones?
- How does the avian pulmonary system work?
- What is a bird’s respiratory system?
- Where do bird mites live in the body?
- What are Sternostoma tracheacolum (air sac mites)?
- Do Canaries get air sac mites?
- What causes air sac mites in birds?
What is an air sac in birds?
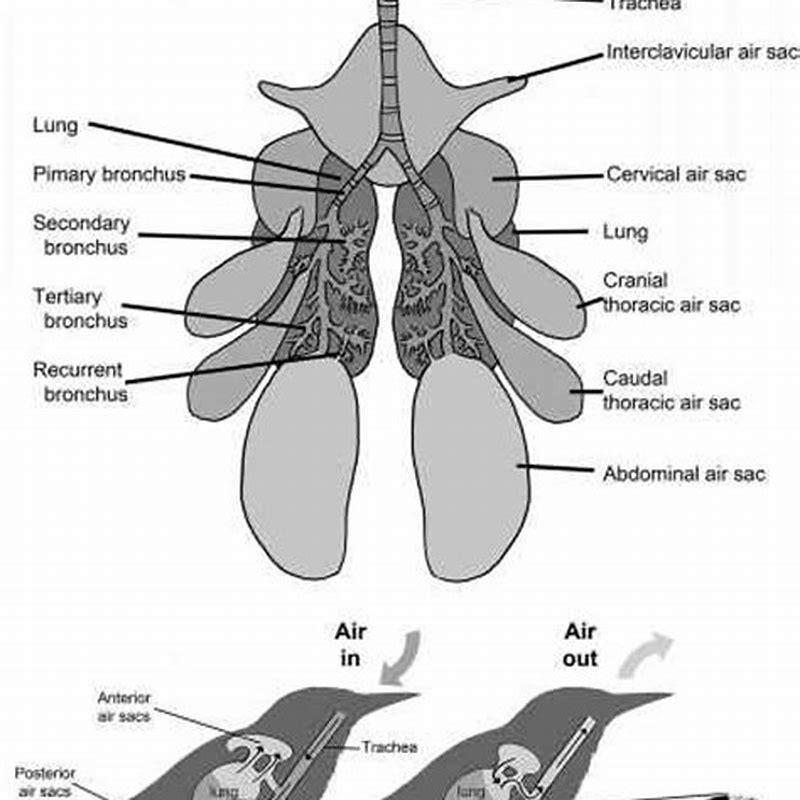
An air sac is part of the bird ‘s respiratory system. It is a series of thin-walled sacs, usually eight or nine, that comprise the system along with the lungs. It makes the bird respiratory system more effective. When the bird inhales, the lungs fill up as well as the air sacs.
Where does the air enter the lungs of a bird?
In bird lungs (A), most air directly enters the caudal air sacs during inspiration (thick black arrow), whereas a lesser part flows through the parabronchi/air capillaries into cranial air sacs (thin black arrows).
What is the function of the anterior air sacs?
Air enters the bird via the trachea. Half of the inhaled air enters the posterior air sacs, the other half passes through the lungs and into the anterior air sacs. Air from the anterior air sacs empties directly into the trachea and out the bird’s mouth or nares. The posterior air sacs empty their air into the lungs.
Which animal has the most air sacs?
Air sac. Air sacs are spaces within an organism where there is the constant presence of air. Among modern animals, birds possess the most air sacs (9–11), with their extinct dinosaurian relatives showing a great increase in the pneumatization (presence of air) in their bones.
What is the pulmonary system in birds?
The avian pulmonary system uses “flow-through ventilation,” relying on a set of nine flexible air sacs that act like bellows to move air through the almost completely rigid lungs. Air sacs do not take part in the actual oxygen exchange, but do greatly enhance its efficiency and allow for the high metabolic rates found in birds.
What are air sac mites in birds?
Air sac mites, or Sternostoma tracheacolum, will get into the respiratory tract of birds (most often canaries and goldfinches, but can be seen in other birds like budgies and cockatiels). These mites can be located in the bird’s trachea, voice box, lungs and air sacs.
What is an air sac and why is it important?
The air sacs fill and empty in two cycles as they take each breath. Therefore, it is important to treat your bird immediately to enable efficient breathing. Birds are unique; they have several air sacs located in their body which if ruptured, leads to an accumulation of air under their skin.
What is the function of the air sacs in a bird?
The avian respiratory system includes the trachea, lungs and a network of air sacs, which function as bellows to ventilate the lungs. These air sacs consist of a very thin membrane that can be punctured by physical trauma such as predator attack or a collision injury.
What is the respiratory system of a bird?
Body systems. Birds have lungs, but they also have air sacs. Depending upon the species, the bird has seven or nine air sacs. Birds do not have a diaphragm; instead, air is moved in and out of the respiratory system through pressure changes in the air sacs. Muscles in the chest cause the sternum to be pushed outward.
Why do bird lungs have more oxygen than mammal lungs?
As a result, air coming into a mammal’s lungs is mixed with ‘old’ air (air that has been in the lungs for a while) & this ‘mixed air’ has less oxygen. So, in bird lungs, more oxygen is available to diffuse into the blood ( avian respiratory system ). Pulmonary air-sac system of a Common Teal ( Anas crecca ). a.
What happens to the spent air in the anterior air sacs?
Instead, the spent air from the lungs enters anterior (forward) air sacs. Then, during the second exhalation, the spent air in the anterior sacs and in the lungs flows out through the trachea, and fresh air in the posterior sacs enters the lungs for gas exchange. In the left panel, yellow oxygen is inhaled through the lungs and into air sacs.
What is the role of the respiratory system in birds?
A finely tuned respiratory system that moves air in one direction enables birds’ high activity level. And the air sacs help regulate temperature by providing a mechanism to dissipate excess body heat. The system is yet another example of the amazing biology of birds.
What is the function of air sacs in the lungs?
Air sacs are found as tiny sacs off the larger breathing tubes (tracheae) of insects, as extensions of the lungs in birds, and as end organs in the lungs of certain other vertebrates. They serve to increase respiratory efficiency by providing a large surface area for gas exchange. See also pulmonary alveolus. Click to see full answer.
Why do birds have air sacs in their lungs?
So, in bird lungs, more oxygen is available to diffuse into the blood ( avian respiratory system ). Pulmonary air-sac system of a Common Teal ( Anas crecca ). a. Latex injection (blue) highlighting the location of air sacs.
How many air sacs does a bird have?
The bird has a number of thin walled, easily distensible air sacs which can extend to approximately 10x the volume of the lungs. Theye are present within body cavities, and extend into some specific bones to take the place of the bone marrow.
What animal has the most air pockets in its bones?
Sauropods are well known for the number of air pockets in their bones (especially vertebra), although one theropod, Deinocheirus, shows a rivalling number of air pockets. Birds’ lungs obtain fresh air during both exhalation and inhalation, because the air sacs do all the “pumping” and the lungs simply absorb oxygen.
How does the avian pulmonary system work?
The avian pulmonary system uses “flow-through ventilation,” relying on a set of nine flexible air sacs that act like bellows to move air through the almost completely rigid lungs. Air sacs do not take part in the actual oxygen exchange, but do greatly enhance its efficiency and allow for the high metabolic rates found in birds.
What is a bird’s respiratory system?
A bird’ s respiratory tract is roughly divided into the upper airways (nasal passages, sinuses, and trachea) and lower respiratory tract (lungs and air sacs – translucent membranes within the bird’s chest, abdomen, and inside some of their bones). Birds with infections of the trachea may show nothing more than a voice change.
Where do bird mites live in the body?
These mites can be located in the bird’s trachea, voice box, lungs and air sacs. All of the different stages of the mites can be located within the respiratory tissues.
What are Sternostoma tracheacolum (air sac mites)?
According to Sherman M. Hoppes, a veterinarian and author of Parasitic Diseases of Pet Birds, ” Sternostoma tracheacolum [air sac mites] parasitizes the entire respiratory tract, most frequently of canaries and gouldian finches. The mites are found in the trachea, syrinx, lungs, and air sacs.
Do Canaries get air sac mites?
The parasites can be present all the way from the nose of the infected bird to the tiny air sacs in the lungs. Canaries and Gouldian finches are two types of birds that commonly suffer from air sac mites. The symptoms of birds with air sac mites are dependent on the severity of the parasitic infection.
What causes air sac mites in birds?
Air Sac Mite Infection in Birds. Birds suffer from lung and airway disorders, which can be caused by a variety of respiratory parasites. One such parasitic infection in birds is caused by air sac mites, which affects the entire respiratory tract.