- What did Linnaeus mean by phylogenetic classification?
- What does this phylogenetic tree show?
- What is the classification of species in biology?
- What is the difference between nodes and branches in phylogenetic tree?
- What is the taxonomy of Linnaeus?
- What is the difference between a phylogenetic tree and a clade?
- Why is the Linnaean classification system the best?
- What is the scientific classification of a species?
- What is a phylogenetic tree in biology?
- What is the difference between nodes and tips on a phylogenetic tree?
- What is phylogeny?
- What is the phylogenetic classification system?
- What is a phylogenetic tree of organisms?
- What is the difference between node-based and branch-based clades?
- What does edge mean in phylogenetic tree?
- What are the alternatives to Linnaean taxonomy?
- What is a clade in biology?
- What is the phylogenetic tree of vertebrates?
- What is the difference between cladogram and phylogenetic tree?
- Where is the last common ancestor on a phylogenetic tree?
- What is Carolus Linnaeus’ taxonomy?
- How many species did Linnaeus discover?
- What is a scaled phylogenetic tree?
- What is a phylogenetic clade?
- What do the branches of a phylogenetic tree represent?
What did Linnaeus mean by phylogenetic classification?
Phylogenetic Classification Linnaeus classified organisms based on obvious physical traits. Basically, organisms were grouped together if they looked alike. After Darwin published his theory of evolution in the 1800s, scientists looked for a way to classify organisms that showed phylogeny.
What does this phylogenetic tree show?
This phylogenetic tree shows how three hypothetical species are related to each other through common ancestors. Do you see why Species 1 and 2 are more closely related to each other than either is to Species 3? One way of classifying organisms that shows phylogeny is by using the clade.
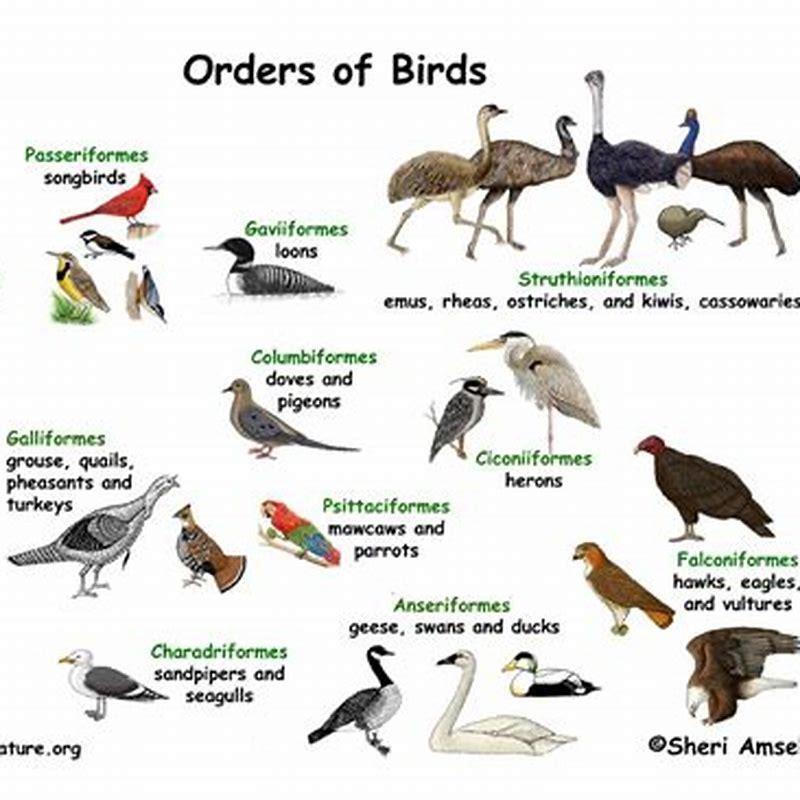
What is the classification of species in biology?
Species are classified into a hierarchical system based on more taxonomical categories. From the highest to the lowest category, organisms can be classified in: Domain> Kingdom> Phylum> Class> Order> Family> Genus> Species> Subspecies> Variety> Form.
What is the difference between nodes and branches in phylogenetic tree?
A branch represents the evolutionary history of a group of organisms, and a node represents the common ance stor of an entire phylogeny . O Crocodiles, birds, and lizards have the same, most-recent common ancestor. Click to see full answer. Simply so, what do the nodes and branches of a phylogenetic tree indicate?
What is the taxonomy of Linnaeus?
In the taxonomy of Linnaeus there are three kingdoms, divided into classes, and they, in turn, into lower ranks in a hierarchical order. a term for rank-based classification of organisms, in general. That is, taxonomy in the traditional sense of the word: rank-based scientific classification.
What is the difference between a phylogenetic tree and a clade?
It is represented by a phylogenetic tree that shows how species are related to each other through common ancestors. A clade is a group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all of its descendants. It is a phylogenetic classification, based on evolutionary relationships. What is a clade? What is cladistics, and what is it used for?
Why is the Linnaean classification system the best?
The Linnaean system has proven robust and it remains the only extant working classification system at present that enjoys universal scientific acceptance. However, although the number of ranks is unlimited, in practice any classification becomes more cumbersome the more ranks are added.
What is the scientific classification of a species?
In scientific classification, a species living or having lived is designated following the rules of binomial nomenclature, established by Carl von Linne in the eighteenth century. According to this classification, the name of a species consists of a binomial Latin name that combines the genre with one or two specific epithets.
What is a phylogenetic tree in biology?
A phylogenetic tree shows inferred relationships between different biological species based on based upon similarities or differences in their physical or genetic characteristics.
What is the difference between nodes and tips on a phylogenetic tree?
The tips of the tree represent groups of descendent taxa (often species) and the nodes on the tree represent the common ancestors of those descendants. Additionally, what is the difference between a branch and a node on a phylogenetic tree? Figure 3: Phylogenetic terminology.
What is phylogeny?
Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of group of related organisms. It is represented by a phylogenetic tree that shows how species are related to each other through common ancestors.
What is the phylogenetic classification system?
This phylogenetic classification system names only clades — groups of organisms that are all descended from a common ancestor. As an example, we can look more closely at reptiles and birds. Tree adapted from Irisarri, I., Baurain, D., Brinkmann, H., Delsuc, F., Sire, J.-Y., Kupfer, A., … and Philippe, H., 2017.
What is a phylogenetic tree of organisms?
A phylogeny, or evolutionary tree, represents the evolutionary relationships among a set of organisms or groups of organisms, called taxa (singular: taxon). The tips of the tree represent groups of descendent taxa (often species) and the nodes on the tree represent the common ancestors of those descendants.
What is the difference between node-based and branch-based clades?
(3) “A node-based clade is a clade originating with a particular node on a phylogenetic tree, where the node represents a lineage at the instant of a splitting event.” (4) “A branch-based clade is a clade originating with a particular branch (internode) on a phylogenetic tree, where the branch represents a lineage between two splitting events.”
What does edge mean in phylogenetic tree?
A branch is called an edge, and represents the time estimate of the evolutionary relationships among the taxonomic units. One branch can connect only two nodes. In a phylogenetic tree, the terminal nodes represent the operational taxonomic units (OTUs) or leaves.
What are the alternatives to Linnaean taxonomy?
Alternatives to Linnaean Taxonomy. While the genus and species names of Linneaus’ rank-based classification system are used, cladististic systematics is increasingly popular. Cladistics categorizes organisms based on traits that can be traced to the most recent common ancestor. Essentially, it’s classification based on similar genetics.
What is a clade in biology?
A clade is a group of species used in cladograms (and phylogenetic trees), which consists of one ancestor and all its descendants. The term clade comes from the Greek word klados, which means branch.
What is the phylogenetic tree of vertebrates?
The phylogenetic tree below shows the relationships of seven types of vertebrates, one of which is the extinct dinosaur Tyrannosaurus rex. Notice how each differently colored polygon represents a monophyletic group (clade): a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Each nested monophyletic group represents a different level of classification.
What is the difference between cladogram and phylogenetic tree?
A Cladogram is a diagram used in cladiastics, it shows hypothetical relationships between groups of organisms. A Phylogenetic tree is a diagram used to depict evolutionary relationships among organisms or group of organisms. A Cladogram consists of the organisms being studied, lines and nodes where those lines cross.
Where is the last common ancestor on a phylogenetic tree?
Cladogram (family tree) of a biological group. The last common ancestor is the vertical line stem at the bottom. The blue and red subgroups are clades; each shows its common ancestor stem at the bottom of the subgroup branch.
What is Carolus Linnaeus’ taxonomy?
Put simply, Carolus Linnaeus’ taxonomy is the study of biological diversity. Of the 1.5 million species named, most of these are insects (750,000) other invertebrates (250,000), plants (260,000), and algae, bacteria, fungi, protozoa (220,000). In comparison there are known 40,000 species of fish, 9,600 birds, and only 4,500 mammals.
How many species did Linnaeus discover?
Six years later he published Systema Naturae which included 4,400 species of animals as well as 7,700 species of plants. In 1761, the King of Sweden honored Linnaeus by making him a nobleman. From that time on, he was also known as Carl von Linné. When Linnaeus died in 1778, he was famous throughout Europe.
What is a scaled phylogenetic tree?
A scaled phylogenetic tree, or phylogram, is a tree that depicts the amount of time between each generation or node. A rooted phylogenetic tree shows the relationship of all taxa on the tree to a common ancestor.
What is a phylogenetic clade?
Instead, the clades designated by different kinds of phylogenetic definitions “are fundamentally similar in being conceptualized and defined as parts of phylogeny each of which is composed of an ancestor and all of its descendants” ( de Queiroz 2007, p. 957).
What do the branches of a phylogenetic tree represent?
In all three diagrams, the branches of the trees represent lineage segments (species), and the nodes represent speciation events. Species included in the relevant group or clade are represented by thicker branches. Erroneously and correctly inferred clade compositions under node-based definitions on a lineage tree.