- How do you get rid of ergots?
- Where is the ergot on a horse?
- How do you get rid of ergots on a horse?
- What is ergot on a horse?
- How to get rid of ergots on horses hooves?
- Can you see ergot on a horse?
- What are ergot alkaloids?
- Do all horses have ergots?
- What are the symptoms of ergot toxicity in horses?
- What plants contain ergoline alkaloids?
- How is ergot alkaloid toxicity diagnosed in cattle?
- What are the signs and symptoms of ergot alkaloid toxicity in horses?
- Do horses have ergots on all legs?
- What is ergotism in horses?
- Is ergot alkaloid toxic to horses?
- What is ergot poisoning?
- What are the symptoms of ergot poisoning in horses?
- How much Ergovaline is toxic to cattle?
- How much Ergot does it take to kill a cow?
- What are the effects of ergot on animals?
How do you get rid of ergots?
Very small ergots that don’t extend much and don’t grow much may feel like a callous or some sort of skin funk starting to happen. Just use your fingernails to peel the outer layers away. Your Farrier might also be able to trim them for you.
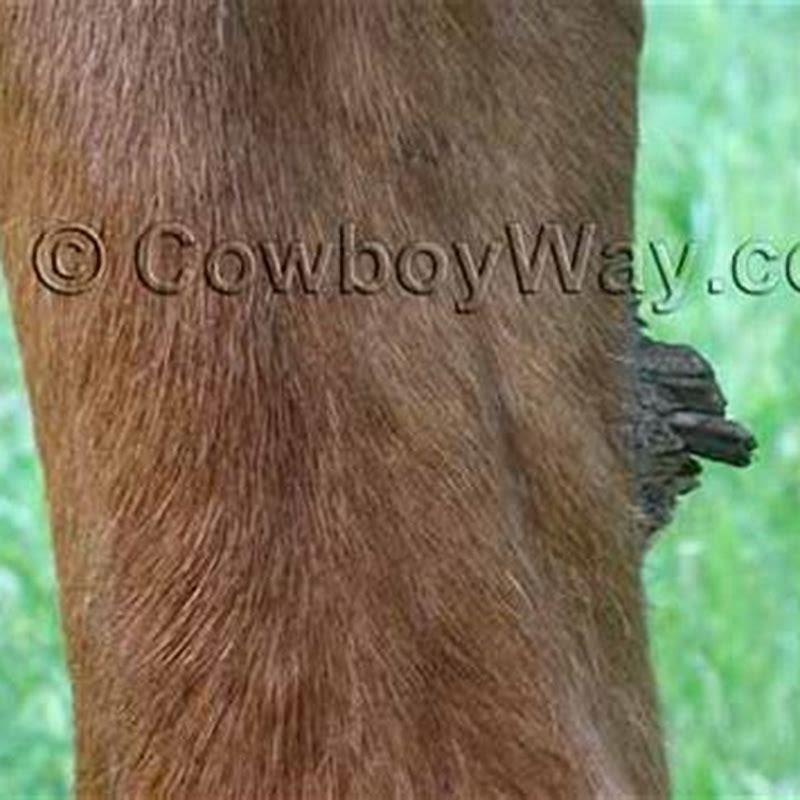
Where is the ergot on a horse?
On the rear legs, they are located just below the hock. The ergot is another callous type growth located on the backside of the fetlock. It is the size of and shaped similar to a pencil eraser. Don’t confuse these with ergot alkaloids, which is a compound found in some fungi and can be toxic to horses.
How do you get rid of ergots on a horse?
Very small ergots that don’t extend much and don’t grow much may feel like a callous or some sort of skin funk starting to happen. Just use your fingernails to peel the outer layers away. Your Farrier might also be able to trim them for you. Again, using a blade might be dangerous for your horse and your hands.
What is ergot on a horse?
The ergot is another callous type growth located on the backside of the fetlock. It is the size of and shaped similar to a pencil eraser. Don’t confuse these with ergot alkaloids, which is a compound found in some fungi and can be toxic to horses.
How to get rid of ergots on horses hooves?
Ergots can often be pinched off with fingernails above the skin. Resist the temptation to twist the ergot as you pinch it, as this might be uncomfortable for the horse and you could get kicked or stomped. Ergots can also be clipped (hoof nippers are handy for this) or trimmed with a knife.
Can you see ergot on a horse?
Ergots can vary in size from horse to horse. If there is long hair on the fetlock, the ergot can be hard to see. One theory science has of the origin of chestnuts and ergot came from, which some may argue or discredit, concerns the evolution of the horse.
What are ergot alkaloids?
Ergot alkaloids are a naturally occurring chemical compound that is most frequently found in large concentrations in the fungi in the Claviceps family. These fungi tend to infest the types of grains and cereals that horses consume, and when ingested in large enough quantities can cause tremors, loss of coordination,…
Do all horses have ergots?
Not all horses have ergots, and some horses may have them only on one or two of their legs. If your animals have ergots, they are on the back area of the horse’s fetlock, usually covered by its hair. Because the hair is usually long in this spot, ergots are often challenging to see.
What are the symptoms of ergot toxicity in horses?
Symptoms of Ergot Alkaloid Toxicity in Horses. The symptoms of ergot alkaloid toxicity can occur suddenly in the case of acute toxicity or gradually over a few days if the amount being consumed is moderate but continuous. Symptoms can include: Convulsion. Death. Delirium. Gangrene in limbs. Loss of appetite.
What plants contain ergoline alkaloids?
Although ergot fungi are the usual source of toxicity from ergoline alkaloids, a few other plants, including the acremonium coenephialum fungus and some types of morning glory also contain this alkaloid. When eaten in large enough quantities this can cause fescue poisoning, which is very similar in behavior to ergot poisoning.
How is ergot alkaloid toxicity diagnosed in cattle?
The preliminary diagnosis of ergot alkaloid toxicity is usually made on the basis of the clinical symptoms, and confirmed by analysis of the animal’s feed as well as their pasture area.
What are the signs and symptoms of ergot alkaloid toxicity in horses?
The primary clinical signs of ergot alkaloid poisoning in the late-gestation mare include: an extended gestation length from 11 to 12 months, dystocia, with mares sometimes trying to foal for many hours,
Do horses have ergots on all legs?
Some horses have them on all four legs, and others don’t have ergots at all. Chestnuts are unique to each and every horse, much like a human fingerprint.
What is ergotism in horses?
There are four forms of ergotism which can occur in horses, these include: gangrenous or cutaneous, hyperthermic, reproductive, and convulsive. Associated with long-term ingestion of ergot-contaminated feedstuff. Results in the restriction of blood flow to parts of the body, causing tissue death, sloughing and foul odor from rotting flesh.
Is ergot alkaloid toxic to horses?
Causes of Ergot Alkaloid Toxicity in Horses. The neurotropic effect that this compound has on most mammals, which causes the tremors, loss of coordination, and delirium, was used in one of its derivatives, LSD.
What is ergot poisoning?
Ergot poisoning- The most frequent culprit that causes ergot alkaloid toxicity is the fungi in the Claviceps family. It is most often found in the form of Claviceps purpura (rye ergot fungus), which is parasitic to several types of grass and cereal, most notably rye grass.
What are the symptoms of ergot poisoning in horses?
The primary clinical signs of ergot alkaloid poisoning in the late-gestation mare include: an extended gestation length from 11 to 12 months, dystocia, with mares sometimes trying to foal for many hours, agalactia (little or no milk) with poor quality colostrum (low immunoglobulin levels),
How much Ergovaline is toxic to cattle?
Ergovaline ranges from 100 to 500 ppb in infected tall fescue, and >200 ppb is considered to be sufficient to cause toxicosis in animals grazing the pasture. Horses are the most susceptible to tall fescue toxicosis, followed by cattle and lastly by sheep.
How much Ergot does it take to kill a cow?
Levels of ergot fed at 0.02% of body weight fed for 11 days resulted in gangrenous ergotism in cattle. That equates to a bit over three ounces per day for a 1,000-pound cow. In general, 0.5% ergot in the ration has resulted in poor-doers, and rates between 0.3% and 1.0% of the ration resulted in gangrenous ergotism when fed for several weeks.
What are the effects of ergot on animals?
All domestic animals are susceptible to the effects of ergot; however, due to their diets, ruminants are usually more commonly affected than others. The ergot bodies contain several toxic chemicals produced by the fungus, called ergot alkaloids.