- Are vertebrates diapsids or synapsids?
- Are lizards considered synapsids?
- How many types of diapsids are there?
- What are synapsid reptiles and mammals?
- Is a diapsid a reptile or amphibian?
- How many species of birds and reptiles are in the diapsids?
- What are the two groups of synapsids?
- What is the difference between synapsids and diapsids?
- What are synapsids and sauropsids?
- What is the difference between a synapsid and a diapsid?
- Are mammals diapsids or synapsids?
- What is a Synapsid reptile?
- Is Reptilia a synapsida?
- What are synapsids now called?
- Is Sauropsida a mammal or a reptile?
- What is the difference between synapsids and sauropsids?
- Are mammals like reptiles a paraphyletic term?
- Is Reptilia the same as Sauropsida?
- What is Sauropsida?
- What is a mammal-like reptile?
- Is the paraphyletic Reptilia monophyletic Sauropsida?
- What is the difference between reptiles and Sauropsida?
- Where did the term sauropsids come from?
- Are birds and mammals reptiles or mammals?
- Are Reptiles Prehistoric?
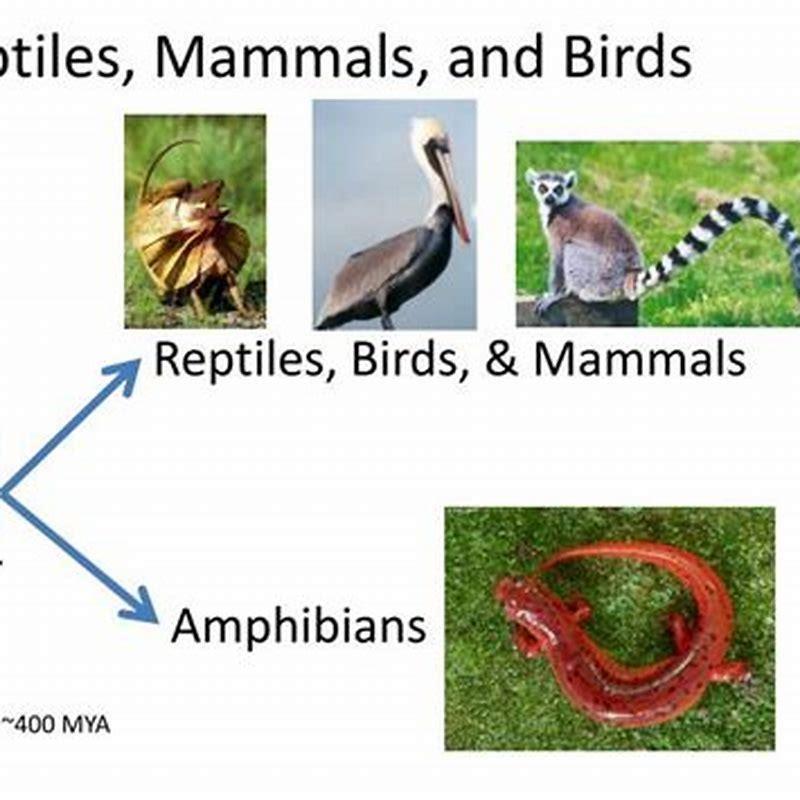
Are vertebrates diapsids or synapsids?
Diapsid is a vertebrate that possesses two major holes known as temporal fenestrae in their skull while synapsid is a vertebrate that possesses only one hole in each side of their skull around the temporal bone. Most reptiles and all the birds are diapsids while most mammals are synapsids. Click to see full answer. Then, are humans Synapsids?
Are lizards considered synapsids?
Also, are lizards Synapsids? Extant reptiles include lizards, snakes, turtles, the worm-like amphisbaenians, crocodiles, and birds, while monotreme, marsupial, and placental mammals are the extant representatives of Synapsida.
How many types of diapsids are there?
Diapsid. Although some diapsids have lost either one hole (lizards), or both holes (snakes and turtles), or have a heavily restructured skull (modern birds), they are still classified as diapsids based on their ancestry. At least 7,925 species of diapsid reptiles exist in environments around the world today (nearly 18,000 when birds are included).
What are synapsid reptiles and mammals?
Synapsid Reptiles and Mammals Synapsid reptiles and the mammals that evolved from them form one monophyletic clade. There are two groups of synapsid reptiles, the pelycosaurs and the therapsids, the latter of which includes an advanced group known as the cynodonts.
Is a diapsid a reptile or amphibian?
Some modern studies of reptile relationships have preferred to use the name “diapsid” to refer to the crown group of all modern diapsid reptiles but not their extinct relatives. However, many researchers have also favored a more traditional definition that includes the prehistoric araeoscelidians.
How many species of birds and reptiles are in the diapsids?
There are more than 14,600 extant species of birds and reptiles included in diapsids. That means; they are an extremely diversified group of animals, including crocodiles, lizards, snakes, tuatara, and birds.
What are the two groups of synapsids?
There are two groups of synapsid reptiles, the pelycosaurs and the therapsids, the latter of which includes an advanced group known as the cynodonts. From anapsid reptiles evolved two groups of higher reptiles: the synapsids (which would lead to mammals) and the diapsids (which would lead to crocodiles, pterosaurs, dinosaurs, and birds).
What is the difference between synapsids and diapsids?
Synapsids are a class of animals that includes mammals and everything more closely related to mammals than to reptiles and birds. They have single skull opening (called the temporal fenestra) behind each eye. Diapsids are a group of reptiles that developed two holes on each side of their skulls. Considering this, what is a Diapsid skull?
What are synapsids and sauropsids?
Synapsids evolved from basal amniotes and are one of the two major groups of amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptiles and birds. The distinctive temporal fenestra developed in the ancestral synapsid about 318 million years ago, during the Late Carboniferous period.
What is the difference between a synapsid and a diapsid?
Diapsid is a vertebrate that possesses two major holes known as temporal fenestrae in their skull while synapsid is a vertebrate that possesses only one hole in each side of their skull around the temporal bone. Most reptiles and all the birds are diapsids while most mammals are synapsids. Click to see full answer.
Are mammals diapsids or synapsids?
Most reptiles and all the birds are diapsids while most mammals are synapsids. Click to see full answer. Then, are humans Synapsids? Humans are synapsids, as well.
What is a Synapsid reptile?
At the turn of the 20th century synapsids were thought to be one of the four main subclasses of reptiles. They were differentiated from other reptiles by their distinctive temporal openings. These openings in the skull bones allowed the attachment of larger jaw muscles, hence a more efficient bite.
Is Reptilia a synapsida?
Additionally, Reptilia has been revised into a monophyletic group and is considered entirely distinct from Synapsida, being the sister group of Synapsida within Amniota. Although Synapsida includes modern mammals, the term is most often used when referring to non-mammalian, non- therapsid synapsids.
What are synapsids now called?
They are now more correctly referred to as stem mammals or proto-mammals. Synapsids evolved from basal amniotes and are one of the two major groups of amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptiles and birds.
Is Sauropsida a mammal or a reptile?
Sauropsida is the sister taxon to Synapsida, the clade of amniotes which includes mammals as its only modern representatives. Although early synapsids have historically been referred to as “mammal-like reptiles,” all synapsids are more closely related to mammals than to any modern reptile.
What is the difference between synapsids and sauropsids?
Although early synapsids have historically been referred to as “mammal-like reptiles,” all synapsids are more closely related to mammals than to any modern reptile. Sauropsids, on the other hand, include all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals.
Are mammals like reptiles a paraphyletic term?
The term “mammal-like reptiles” includes groups that are not united in this way, which makes it a paraphyletic term. The monophyly of Synapsida is not in doubt, however, and the expressions such as “Synapsida contains the mammals” and “synapsids gave rise to the mammals” both express the same phylogenetic hypothesis.
Is Reptilia the same as Sauropsida?
Since the advent of phylogenetic nomenclature, the term Reptilia has fallen out of favor with many taxonomists, who have used Sauropsida in its place to include a monophyletic group containing the traditional reptiles and the birds.
What is Sauropsida?
Sauropsida (“lizard faces”) is a group ofamniotes that includes all existing birdsand reptiles as well as their fossil ancestors and other extinct relatives. Large land animals are either in this group or in its sister group, Synapsida, which includes mammals and their fossil relatives.
What is a mammal-like reptile?
Mammal-like reptiles is a term used to describe the prehistoric animals that appear to be the reptilian ancestors of mammals. They were the dominant terrestrial animals by the Middle Permian period.
Is the paraphyletic Reptilia monophyletic Sauropsida?
Despite the early proposals for replacing the paraphyletic Reptilia with a monophyletic Sauropsida, which includes birds, that term was never adopted widely or, when it was, was not applied consistently.
What is the difference between reptiles and Sauropsida?
A definition in accordance with phylogenetic nomenclature, which rejects paraphyletic groups, includes birds while excluding mammals and their synapsid ancestors. So defined, Reptilia is identical to Sauropsida . Though few reptiles today are apex predators, many examples of apex reptiles have existed in the past.
Where did the term sauropsids come from?
All living sauropsids are members of the sub-group Diapsida, the Parareptilia clade having died out 200 million years ago. The term originated in 1864 withThomas Henry Huxley, [1] who grouped birds with reptiles based on fossil evidence.
Are birds and mammals reptiles or mammals?
All terrestrial vertebrates are therefore classified as ‘tetrapods’ and all tetrapods except amphibians as ‘reptiliomorphs’, including therefore birds and mammals. Modern reptiles, birds and mammals are later branches in the reptiliomorph tree. The question, then, is how strong is the evidence that ancient ‘reptiliomorphs’ evolved into mammals?
Are Reptiles Prehistoric?
Many species of reptiles look a little prehistoric. In fact, most dinosaurs could be classified as reptiles, and reptilian fossils that date back to over 300 million years. Reptiles existed well before any of the mammals we know today.