- What is the Crocodylomorpha?
- How did crocodylomorphs survive the K-Pg extinction event?
- What happened in the Cretaceous period?
- How did dinosaurs adapt to life in the Cretaceous period?
- What happened to cephalopods after the KPG boundary?
- What was the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction?
- Are all crocodiles oviparous?
- What is the Paracrocodylomorpha clade?
- Do crocodiles lay eggs or give birth?
- Why is the Cretaceous period the best known period for dinosaurs?
- What do the fossils found in the Cretaceous rock layer represent?
- What is the timescale of the Cretaceous period?
- What was life like in the Cretaceous period?
- What happened during the Cretaceous Tertiary extinction?
- What animals went extinct in the Devonian period?
- What happened to reptiles before the K–T boundary?
- What happened during the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction?
- How did mammals evolve after the K-Pg extinction?
- What happened to dinosaurs in the Cretaceous-Tertiary era?
- Are fish and insects oviparous?
- Are crocodiles and amphibians the same?
- Are oviparous snakes viviparous?
- What is an example of an oviparous animal?
- Are crocodiles oviparous?
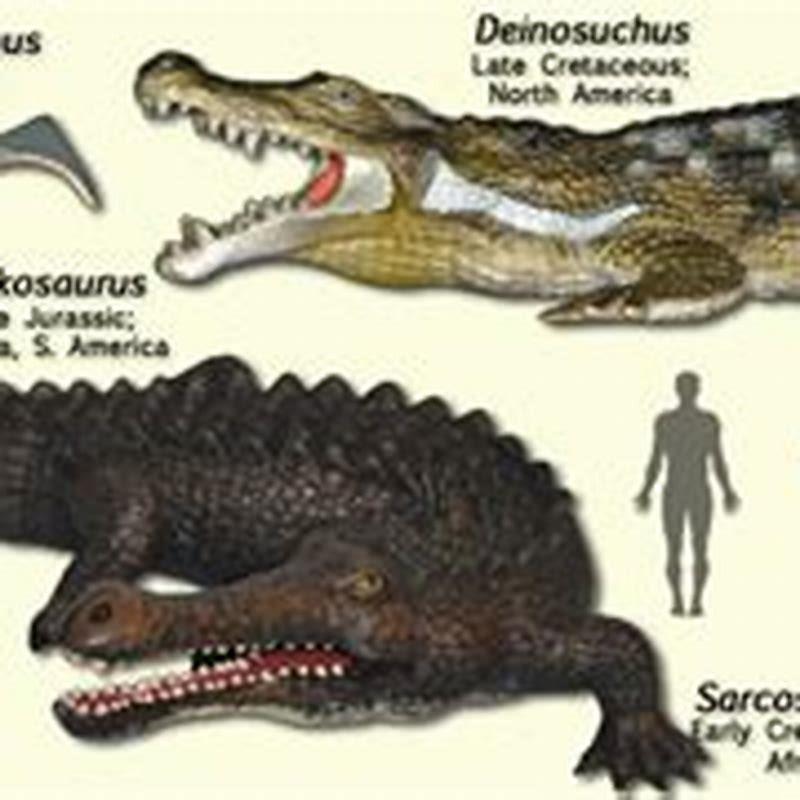
What is the Crocodylomorpha?
The Crocodylomorpha are an important group of archosaurs that include the crocodilians and their extinct relatives. During Mesozoic and Early Tertiary times, the Crocodylomorpha were far more diverse than they are now. Triassic forms were small, lightly built, active terrestrial animals.
How did crocodylomorphs survive the K-Pg extinction event?
During the Jurassic, Crocodylomorphs morphologically diversified into numerous niches, including into the aquatic and marine realms. Their conquest of the these realms may have helped them survive the K-Pg extinction event, like the turtles.
What happened in the Cretaceous period?
The Cretaceous is the last of the three great ages of dinosaurs. To put it in a nutshell, dinosaurs appeared in the Triassic, grew to enormous sizes in the Jurassic and then spent the Cretaceous diversifying into any number of forms before their demise (which will occur in 10 million years time).
How did dinosaurs adapt to life in the Cretaceous period?
The dinosaurs never adapted to life in the sea, and in the Cretaceous oceans the ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs were joined by the mosasaurs. The world was becoming ever-more familiar during the Cretaceous Period, with the continents assuming their current positions and flowering plants making their appearance.
What happened to cephalopods after the KPG boundary?
The numbers of cephalopod, echinoderm, and bivalve genera exhibited significant diminution after the K–Pg boundary. Most species of brachiopods, a small phylum of marine invertebrates, survived the K–Pg extinction event and diversified during the early Paleocene.
What was the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction?
The Cretaceous–Paleogene ( K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary (K–T) extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago.
Are all crocodiles oviparous?
All crocodilians (crocodiles, alligators, caimans, and gharials) are oviparous: they lay eggs. All birds are oviparous as well.
What is the Paracrocodylomorpha clade?
The clade includes the diverse and unusual group Poposauroidea as well as the generally carnivorous and quadrupedal members of Loricata, including modern crocodylians. Paracrocodylomorpha was named by paleontologist J. Michael Parrish in 1993, although the group is now considered to encompass more reptiles than his original definition intended.
Do crocodiles lay eggs or give birth?
Like any other reptile,crocodiles are oviparous (lay eggs).Mammals except for some are only viviparous (give direct birth) 10 things all bosses need to do.
Why is the Cretaceous period the best known period for dinosaurs?
However the Cretaceous is probably best know because some of the best known dinosaurs and other prehistoric reptiles people know about come from that period even if people in general don’t realize they came from the Cretaceous period.
What do the fossils found in the Cretaceous rock layer represent?
The fossils found in the Cretaceous rock layer represent animals that were alive during the Cretaceous Period. By studying the fossils present in Cretaceous rocks, paleontologists can build up a picture of life in the Cretaceous Period.
What is the timescale of the Cretaceous period?
An approximate timescale of key Cretaceous events. Axis scale: millions of years ago. The Cretaceous ( /krɪˈteɪ.ʃəs/, krih-TAY-shəs) is a geologic period and system that spans from the end of the Jurassic Period 145 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Paleogene Period 66 mya.
What was life like in the Cretaceous period?
Cretaceous Period: Life. No great extinction or burst of diversity separated the Cretaceous from the Jurassic Period that had preceded it. In some ways, things went on as they had. Dinosaurs both great and small moved through forests of ferns, cycads, and conifers.
What happened during the Cretaceous Tertiary extinction?
Cretaceous-Tertiary (K-T), or Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg), extinction (about 66.0 million years ago), involving about 80 percent of all animal species, including the dinosaurs and many species of plants.
What animals went extinct in the Devonian period?
Dunkleosteus terrelli is one of the species of armored fish called placoderms that went extinct at the end of the Devonian Period. The brunt of this extinction was borne by marine invertebrates. As in the Ordovician Extinction, many species of corals, trilobites, and brachiopods vanished.
What happened to reptiles before the K–T boundary?
It is important to note that some groups of reptiles died out well before the K–T boundary, including flying reptiles ( pterosaurs) and sea reptiles ( plesiosaurs, mosasaurs, and ichthyosaurs ). Among surviving reptile groups, turtles, crocodilians, lizards, and snakes were either not affected or affected only slightly.
What happened during the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction?
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, was a sudden mass extinction of some three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the exception of some ectothermic species such as the leatherback sea turtle and crocodiles, no tetrapods weighing more than 25 kilograms (55 lb) survived.
How did mammals evolve after the K-Pg extinction?
After the K–Pg extinction, mammals evolved rapidly to fill the niches left vacant by the dinosaurs. Also significant, within the mammalian genera, new species were approximately 9.1% larger after the K–Pg boundary.
What happened to dinosaurs in the Cretaceous-Tertiary era?
Cretaceous-Tertiary (K-T), or Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg), extinction (about 66 million years ago), involving about 80 percent of all animal species, including the dinosaurs and many species of plants.
Are fish and insects oviparous?
– The clown fish ( Amphiprion percula ): Although there are many exceptions, many fish are oviparous. The clownfish, very popular in aquariums, is one example. Members of this species have external fertilization and usually lay several dozen eggs in the same place. – The insects: practically all insects hatch from eggs, that is, they are oviparous.
Are crocodiles and amphibians the same?
It is easy to confuse crocodiles for amphibians as their class, reptiles, and the class amphibians both lay eggs and are cold-blooded. But even in this similarity, there is a dissimilarity.
Are oviparous snakes viviparous?
Snakes that lay their eggs outside of their bodies are known as oviparous. Those that hold them are called ovoviviparous. Ovoviviparous snakes seem to bring forth live youthful, yet they really don’t – despite the fact that there are the individuals who do, known as viviparous snakes Are dolphins viviparous?
What is an example of an oviparous animal?
In reptiles, turtles are an example of oviparous animal. Ovoviviparous means that an animal lays egg but the egg stays in mother’s body. The embryo receives nutrients from yolk sac instead of the mother itself.
Are crocodiles oviparous?
Like any other reptile,crocodiles are oviparous (lay eggs).Mammals except for some are only viviparous (give direct birth) 10 things all bosses need to do. Bosses should find out what is needed to bring out the best in their employees. They are most certainly oviparous.