- What animals are in the tetrapod family?
- Are there any diapsids that are closer to birds than lizards?
- What are some examples of evolution in tetrapods?
- What types of animals are included in the Phylum Pteridophyta?
- What family do reptiles belong to?
- How did Linnaeus classify the tetrapods?
- What type of animal is a tetrapod?
- What was the dominant tetrapod fauna during the Carboniferous period?
- Why don’t crocodiles and lizards get along with birds?
- What are some examples of tetrapods that lose limbs?
- Did tetrapods evolve feet in water?
- What did tetrapods have in common with vertebrates?
- What caused the evolution of tetrapod respiration?
- Which phyla include the phyla Cnidaria and Ctenophora?
- What is the difference between amniotes and tetrapods?
- Why are Carboniferous faunas so different from the Devonian period?
- Are birds and crocodiles related to each other?
- Why don’t birds fly like crocodiles?
- Are dinosaurs close to other reptiles today?
- What characteristics are unique to fish and tetrapods?
- Do any tetrapods lose their limbs?
- Why do some tetrapods have vestigial bones?
- What is an example of a tetrapod?
- What is a tetrapod class?
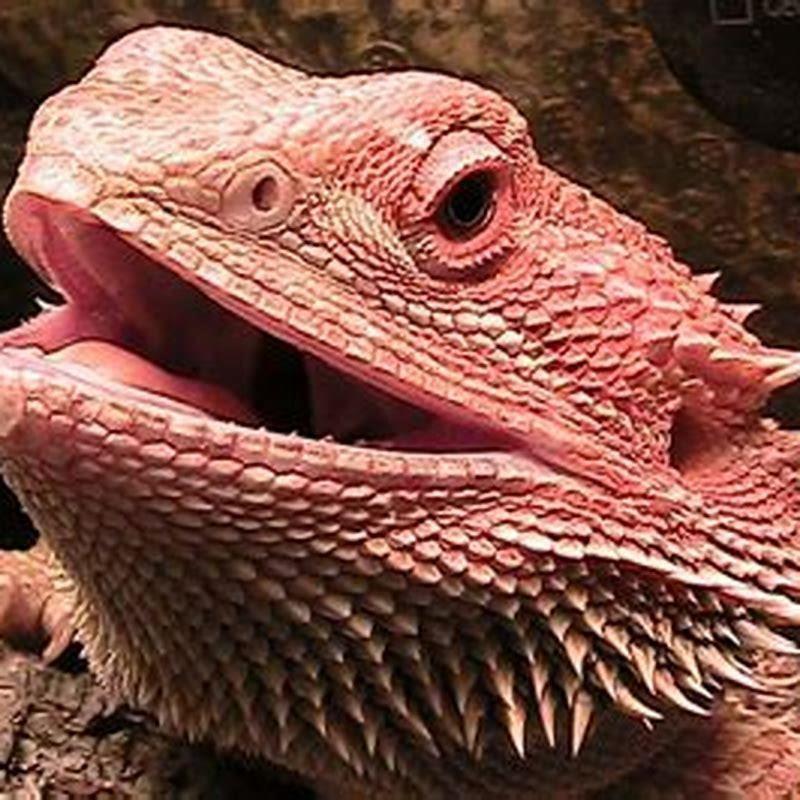
What animals are in the tetrapod family?
Animals and Nature. Tetrapods are a group of vertebrates that includes amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Tetrapods include all living land vertebrates as well as some former land vertebrates that have since adopted an aquatic lifestyle (such as whales, dolphins, seals, sea lions, sea turtles, and sea snakes).
Are there any diapsids that are closer to birds than lizards?
And crcocodiles are closer to birds than lizards. There’s a lot of diapsids, and these include all living reptiles as well as dinosaurs. , Reptile keeper and breeder, wildlife observation and ecology hobbyist.
What are some examples of evolution in tetrapods?
Evolution of tetrapods. Several groups of tetrapods, such as the snakes and cetaceans, have lost some or all of their limbs. In addition, many tetrapods have returned to partially aquatic or fully aquatic lives throughout the history of the group (modern examples of fully aquatic tetrapods include cetaceans and sirenians ).
What types of animals are included in the Phylum Pteridophyta?
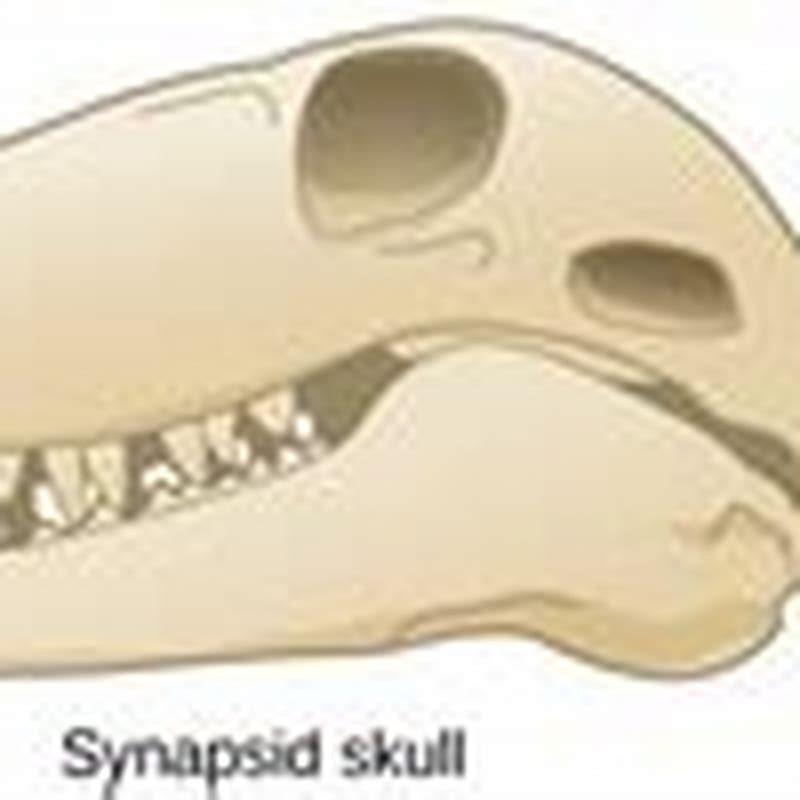
It includes extant and extinct amphibians, reptiles (including dinosaurs and therefore birds ), and synapsids (including mammals ).
What family do reptiles belong to?
What family are reptiles in? Reptiles are tetrapod animals in the class Reptilia, comprising today’s turtles, crocodilians, snakes, amphisbaenians, lizards, tuatara, and their extinct relatives. The study of these traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology.
How did Linnaeus classify the tetrapods?
With the birth of modern biological classification in the 18th century, Linnaeus used the same division, with the tetrapods occupying the first three of his six classes of animals.
What type of animal is a tetrapod?
Tetrapods ( / ˈtɛtrəˌpɒdz /; from Ancient Greek τετρα- (tetra-) ‘four’, and πούς (poús) ‘foot’) are four-limbed animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda ( / tɛˈtrɒpədə / ). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, reptiles (including dinosaurs and therefore birds ), and synapsids (including mammals ).
What was the dominant tetrapod fauna during the Carboniferous period?
With the close of the Carboniferous, the amniotes became the dominant tetrapod fauna. While primitive, terrestrial reptiliomorphs still existed, the synapsid amniotes evolved the first truly terrestrial megafauna (giant animals) in the form of pelycosaurs, such as Edaphosaurus and the carnivorous Dimetrodon.
Why don’t crocodiles and lizards get along with birds?
The problem is that it turns out lizards, crocodiles, and turtles aren’t that related to each other And crcocodiles are closer to birds than lizards. There’s a lot of diapsids, and these include all living reptiles as well as dinosaurs.
What are some examples of tetrapods that lose limbs?
Several groups of tetrapods, such as the snakes and cetaceans, have lost some or all of their limbs. In addition, many tetrapods have returned to partially aquatic or fully aquatic lives throughout the history of the group (modern examples of fully aquatic tetrapods include cetaceans and sirenians ).
Did tetrapods evolve feet in water?
Pelvic bone fossils from Tiktaalik shows, if representative for early tetrapods in general, that hind appendages and pelvic-propelled locomotion originated in water before terrestrial adaptations. Another indication that feet and other tetrapod traits evolved while the animals were still aquatic is how they were feeding.
What did tetrapods have in common with vertebrates?
A single rod opsin, rhodopsin, was present in the first jawed vertebrate, inherited from a jawless vertebrate ancestor: Tetrapods retained the balancing function of the middle ear from fish ancestry. Air vibrations could not set up pulsations through the skull as in a proper auditory organ.
What caused the evolution of tetrapod respiration?
The evolution of early tetrapod respiration was influenced by an event known as the “charcoal gap”, a period of more than 20 million years, in the middle and late Devonian, when atmospheric oxygen levels were too low to sustain wildfires.
Which phyla include the phyla Cnidaria and Ctenophora?
c. The Radiata include the phyla Cnidaria and Ctenophora. d. All nonradiate animals, including the sponges, display bilateral symmetry. a. True b. False c. True d.
What is the difference between amniotes and tetrapods?
Primitive tetrapods, like modern amphibians, need to return to water to lay eggs; in contrast, amniotes, like modern reptiles – whose eggs possess a shell that allows them to be laid on land – were better adapted to the new conditions.
Why are Carboniferous faunas so different from the Devonian period?
The Late Devonian Period experienced major extinctions within some marine invertebrate groups, and Carboniferous faunas reflect a different composition from what had prevailed earlier in the Paleozoic Era.
Are birds and crocodiles related to each other?
In more recent years, scientists have discovered that some reptiles are more closely related to birds than they are to other reptiles (e.g., crocodiles are more closely related to birds than they are to lizards). For this reason, many modern scientists prefer to consider the birds part of Reptilia as well.
Why don’t birds fly like crocodiles?
Part of the problem may lie with how dissimilar birds are, as a group, to their closest relatives, the crocodilians (alligators, crocodiles, caimans, etc.). Most birds are smaller than a human, have feathers covering most of their bodies, and plenty of them fly.
Are dinosaurs close to other reptiles today?
But if you are looking only at living critters, dinosaurs are not close to any reptile living today, although they are a bit closer to crocodilians than to the rest. In fact, despite apperances, crocs are closer to birds (and hence dinosaurs) than to the other reptiles.
What characteristics are unique to fish and tetrapods?
Tiktaalik and Acanthostega are fossil species have characteristics unique to fish as well as characteristics found in fish and tetrapods. Lobe-finned fish have lungs in their body. Their fins is attached to a single bone.
Do any tetrapods lose their limbs?
Some tetrapods, like seals, lost some of their limbs through evolution. Tetrapods are a sub-group of animals known as Sarcopterygii. The term “tetrapod” refers to land-living animals such as hawks, frogs, and turtles.
Why do some tetrapods have vestigial bones?
Some tetrapods, such as the snakes, have lost some or all of their limbs through further speciation and evolution; some have only concealed vestigial bones as a remnant of the limbs of their distant ancestors.
What is an example of a tetrapod?
For example, whales, dolphins, seals, walrus, otters, sea snakes, sea turtles, frogs, and salamanders, are all examples of tetrapods that depend on aquatic habitats for some or all of their life cycle. Several groups of tetrapods have also adopted an arboreal or aerial lifestyle. Such groups include birds, bats, flying squirrels, and flying lemurs.
What is a tetrapod class?
(Show more) tetrapod, (superclass Tetrapoda), a superclass of animals that includes all limbed vertebrates (backboned animals) constituting the classes Amphibia ( amphibians ), Reptilia ( reptiles ), Aves ( birds ), Mammalia ( mammals ), and their direct ancestors that emerged roughly 397 million years ago during the Devonian Period.