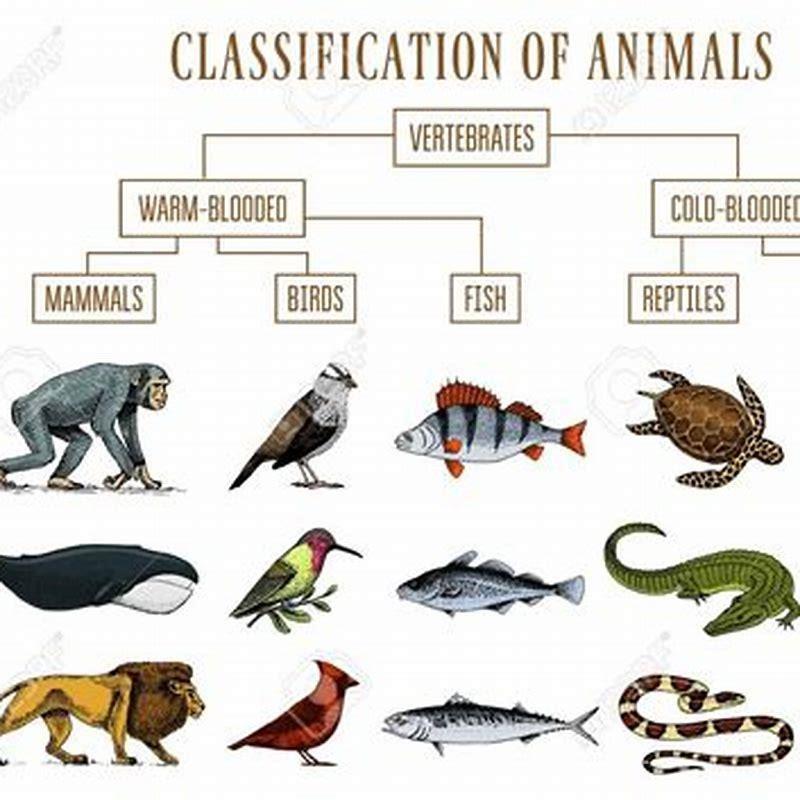
- What is the difference between RBS of birds and mammals?
- What is the difference between mammal and bird respiratory system?
- What is the difference between bats and birds?
- How is the respiratory cycle different in mammals and birds?
- Why are birds not mammals?
- What is the difference between bird blood and mammal blood?
- Why do birds breathe better than mammals?
- What is the difference between the lungs of mammals and birds?
- How are the air capillaries similar and different in mammals and birds?
- How does the avian respiratory system differ from other vertebrates?
- What are the similarities between bats and owls?
- Do bats lay eggs or lay eggs?
- What is the difference between a bird and a bat?
- Do birds see like bats?
- What is the difference between the secondary bronchi of mammals and birds?
- How does the respiratory system differ in mammals and birds?
- Why do mammals and birds need to eat so much food?
- What makes birds stand out from other animals?
- Why do birds not produce milk?
- Why is a bird not a mammal?
- What do human blood and animal blood have in common?
- Is bird blood similar to mammal blood?
- Why do birds have such an efficient circulatory system?
- Why is the blood red in mammals and birds?
- How does a bird’s ventilation cycle differ from that of mammals?
- Are bird lungs more efficient than mammal lungs?
What is the difference between RBS of birds and mammals?
The RBS of birds are oval in shape whereas most of the mammals’ RBSs have a round shape. … When one thinks of the differences between mammals and birds, the first thing that comes to mind is that mammals give birth to their young whereas birds lay eggs.
What is the difference between mammal and bird respiratory system?
• In mammals, the respiratory gas exchanging occurs in alveoli of lungs, whereas in birds it takes place in air capillaries. • Mammals have a single respiratory cycle, but birds have a double respiratory cycle. • Birds have air sacs, but mammals do not.
What is the difference between bats and birds?
Despite their differences bats and birds exist to keep the equilibrium in the environment. They are essential in dispersing seeds (fruits) and important for pollination. • Bats are webbed structured flying animals while birds are feathered winged animals. • Bats are mammals, whereas birds lay eggs.
How is the respiratory cycle different in mammals and birds?
While there is only a single respiratory cycle in mammals, there are two cycles in birds. Now comparing the blood, birds have a nucleus in the RBS whereas it is not generally seen in mammals. If there is a nucleus in the RBS in mammals, then it is a sign of sickness.
Why are birds not mammals?
Besides, birds are warm-blooded and unlike mammals, they lay eggs too. Although few of them are flightless birds but still the entire body of all the bird species is enveloped with plumage. Some people confuse the plumage of birds with hair due to which sometimes they call few birds as mammals.
What is the difference between bird blood and mammal blood?
Now comparing the blood, birds have a nucleus in the RBS whereas it is not generally seen in mammals. If there is a nucleus in the RBS in mammals, then it is a sign of sickness. The RBS of birds are oval in shape whereas most of the mammals’ RBSs have a round shape.
Why do birds breathe better than mammals?
The respiratory system of birds is more efficient than that of mammals, transferring more oxygen with each breath. This also means that toxins in the air are also transferred more efficiently.
What is the difference between the lungs of mammals and birds?
In mammalian lungs, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs in microscopic sacs in the lungs, called ‘alveoli.’ In the avian lung, the gas exchange occurs in the walls of microscopic tubules, called ‘air capillaries.’ The respiratory system of birds is more efficient than that of mammals, transferring more oxygen with each breath.
How are the air capillaries similar and different in mammals and birds?
The air capillaries are similar to microscopic tubes. The respiratory system differs in mammals and birds because the exchange process happens in a single cycle in mammals. In birds, however, the exchange process occurs in 2 different cycles. This means that oxygen is kept in the body for two complete inhalations and exhalations.
How does the avian respiratory system differ from other vertebrates?
The avian respiratory system is different from that of other vertebrates, with birds having relatively small lungs plus nine air sacs that play an important role in respiration (but are not directly involved in the exchange of gases).
What are the similarities between bats and owls?
Another similarity is that there are a few nocturnal bird species, such as owls. Owls also use echolocation to detect food and other objects when flying in the dark. Owls and bats both struggle with light sensitivity, and they have excellent hearing, which helps them hunt at night.
Do bats lay eggs or lay eggs?
Bats are mammals, so they don’t lay eggs, compared to birds that are known as egg-laying animals. When flying, bats don’t flap their forelimbs completely compared to birds. Generally, bats have teeth which help them when eating while birds have beaks in picking up food and eating them.
What is the difference between a bird and a bat?
Birds belong to the class Aves while bats belongs to mamalia and there are morphological differences like fore limbs of birds are modified as wings with feathers while bats have wings with skin (petagium)
Do birds see like bats?
Birds have standard vision; they do not use sound to detect objects like bats, but rather their vision is light-based. Birds detect items from the light that reflects off these surfaces; some birds have more advanced vision, such as hawks and owls. Nocturnal birds can see at night.
What is the difference between the secondary bronchi of mammals and birds?
In contrast to mammals, all the secondary bronchi show relatively little ramification. In both birds and mammals, ventilation is cyclic: during inspiration, air is sucked into the respiratory system, while during expiration, it is expelled.
How does the respiratory system differ in mammals and birds?
The respiratory system differs in mammals and birds because the exchange process happens in a single cycle in mammals. In birds, however, the exchange process occurs in 2 different cycles. This means that oxygen is kept in the body for two complete inhalations and exhalations.
Why do mammals and birds need to eat so much food?
The warm-blooded nature of mammals and birds ensures that they have to consume a significant amount of food to maintain body temperature. The dietary requirements of both these species are much higher than cold-blooded animals such as reptiles.
What makes birds stand out from other animals?
However, birds have an easily identifiable characteristic feature— their feathers— that make them stand out among other animals. Birds are neither mammals nor reptiles; they are warm-blooded vertebrates characterized by their distinctive feature— feathers.
Why do birds not produce milk?
Birds do not have mammary glands to produce milk. This is why birds provide easy to digest food to their younger ones, which they get external to their bodies. There are many differences between mammals and insects.
Why is a bird not a mammal?
They are not mammals even though they are warm-blooded, breathe air, and possess vertebrae, which are other mammalian characteristics. They’re not mammals even though some species gather in flocks for foraging, hunting, childrearing, and protection the way mammals do in herds. Birds exclusively lay eggs.
What do human blood and animal blood have in common?
Both human blood and animal blood have A and B antigens. Both human blood and animal blood comprise different types of respiratory pigments for the transportation of oxygen. The main function of both human blood and animal blood is to transport nutrients, oxygen, and metabolic wastes to their destinations.
Is bird blood similar to mammal blood?
Birds have evolved such a system and it is very similar to a mammal’s. Bird blood is similar to ours, in that it contains both red (erythrocytes) and white blood cells called leucocytes.
Why do birds have such an efficient circulatory system?
Active flapping flight needs a lot of energy to maintain. This, in turn, necessitates an efficient and effective circulatory system. Birds have evolved such a system and it is very similar to a mammal’s. Bird blood is similar to ours, in that it contains both red (erythrocytes) and white blood cells called leucocytes.
Why is the blood red in mammals and birds?
In both cases, the red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which is a protein used by the body to transport oxygen. In both mammals as well as birds, the blood is red due to the presence of hemoglobin. If you want to know the differences between mammals and insects, I have written an article which you can find here.
How does a bird’s ventilation cycle differ from that of mammals?
Most importantly, a bird replaces nearly all the air in its lungs with each breath. No residual air is left in the lungs during the ventilation cycle of birds, as it is in mammals.
Are bird lungs more efficient than mammal lungs?
I have heard it said that bird lungs are more efficient than mammal lungs – the reason given was something to do with one-way flow and their hollow bones. I haven’t been able to find anything understandable about it on the internet – is this true?