- How do pesticides affect the food chain?
- What are the health effects of DDT?
- What did DDT do to the birds?
- How do insect pesticides affect birds?
- What are pesticides and how do they work?
- How do insecticides affect birds?
- How do pesticides affect non-target organisms?
- What animal has the highest level of DDT?
- How does DDT affect the liver?
- Why is DDT considered a carcinogen?
- What are the effects of DDT on animals?
- What was the effect of DDT on birds?
- Is DDT still used today?
- What happens when DDT enters the food chain?
- How do neonicotinoids affect birds?
- How do insect pesticides work?
- What are the negative effects of pesticides on birds?
- How can farmers protect birds from pesticides and herbicides?
- Are there pesticides in the air?
- What are pesticides doing to birds?
- How many pesticides are there in a bird nest?
- How do insecticides affect the environment?
- What are pesticides and why are they bad?
- How do pesticides harm fish?
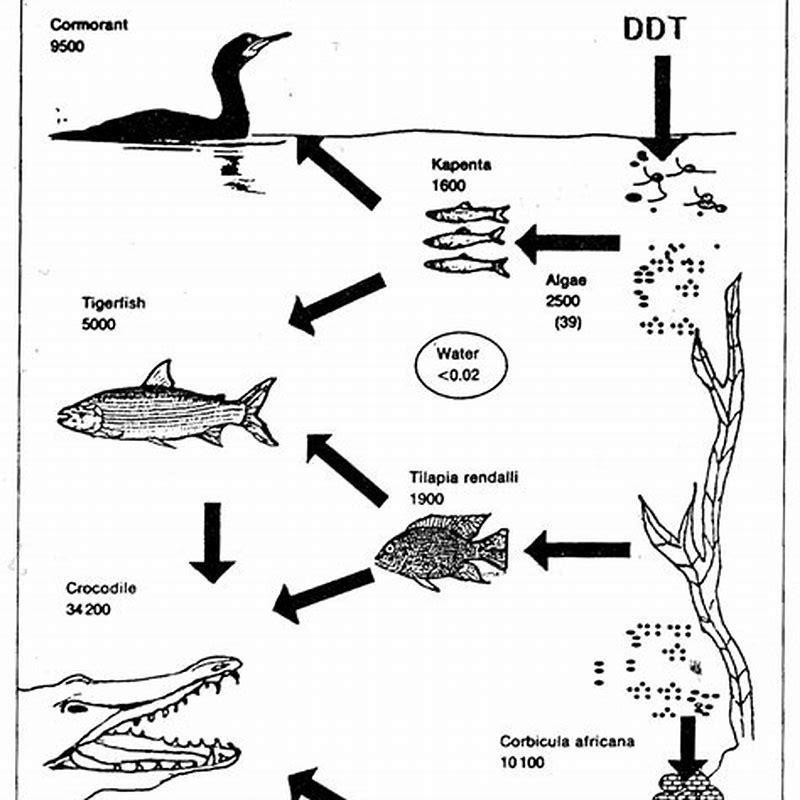
How do pesticides affect the food chain?
At each trophic level of the food chain, the amount of D.D.T. accumulating in the organisms’ tissues magnifies. Unfortunately for birds, many of their eggshells became weakened due to this pesticide and reproductive failure of the embryos occurred.
What are the health effects of DDT?
These DDT residues caused both acute and chronic health problems. DDT caused direct mortality of some birds by poisoning their nervous system even in birds like robins that feed relatively low on the food chair.’ (See article beginning on p.)
What did DDT do to the birds?
DDT and its metabolites cause eggs to have thin shells and reduce levers of a hormone necessary for female birds to lay eggs.4 Population declines and local disappearance of peregrine falcons, bald and golden eagles, ospreys, kestrels, and other predatory birds were recorded. DDT’s history certainly paints a frightening picture.
How do insect pesticides affect birds?
Pesticides injure birds both directly and indirectly, and birds are often affected by a combination of different kinds of effects. For the birds’ own sake, and because, like the miner’s canary, they can warn us when our own health or the health of our ecosystem is threatened, these effects are worth our attention and action.
What are pesticides and how do they work?
Pesticides are chemicals designed to kill invertebrates, usually insects, which have become plant pests. Farmers and gardeners have been spraying their crops and flowers for years to protect them.
How do insecticides affect birds?
Pesticides can also affect birds indirectly by either reducing the amount of available food or altering habitat. Birds that eat insects are literally at a loss when insecticides cause a drop in the number of insect prey available, especially when they have young to feed.
How do pesticides affect non-target organisms?
In addition to killing insects or weeds, pesticides can be toxic to a host of other organisms including birds, fish, beneficial insects, and non-target plants. Insecticides are generally the most acutely toxic class of pesticides, but herbicides can also pose risks to non-target organisms. Surface water contamination
What animal has the highest level of DDT?
The bodies of animals near the top of the food chain, such as predatory birds like eagles, hawks, pelicans, condors and other meat-eating birds, often have the highest DDT levels. Hypersensitive to stimulation, a sensation of prickling, tingling or creeping on skin.
How does DDT affect the liver?
According to the EPA, DDT can cause liver damage including liver cancer, nervous system damage, birth defects, and other reproductive harm. Items that can contain DDT DDT was used to control insect vectors of disease, especially malaria. DDT was used to control pests like mosquitoes, houseflies, body lice, Colorado beetles, and gypsy moths.
Why is DDT considered a carcinogen?
This substance is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on evidence of carcinogenicity in experimental animals. DDT also has serious health effects on humans. According to the EPA, DDT can cause liver damage including liver cancer, nervous system damage, birth defects, and other reproductive harm.
What are the effects of DDT on animals?
Organ toxicity: Acute human exposure data and animal studies reveal that DDT can affect the nervous system, liver and kidney. Fat in humans and animals: DDT is very slowly transformed in animal systems. Effects on birds: DDT may be slightly toxic to almost non-toxic in birds.
What was the effect of DDT on birds?
One of the major effects of DDT, and one that led in many ways to its ban was the effect it had on the eggshells of predatory birds. Because they are such a visible member of the animal kingdom, much more than fish or other underwater life, people noticed when the populations dropped precipitously.
Is DDT still used today?
Some organochlorine pesticides for example, the miticide dicofol which also causes eggshell thinning in birds 6 are still used in the United States, and uses of others (for example, chlordane) were restricted or cancelled much later than DDT.5 In addition, DDT and related compounds are still used in many other countries.
What happens when DDT enters the food chain?
It enters food chains and bioaccumulation occurs. At each trophic level of the food chain, the amount of D.D.T. accumulating in the organisms’ tissues magnifies. Unfortunately for birds, many of their eggshells became weakened due to this pesticide and reproductive failure of the embryos occurred.
How do neonicotinoids affect birds?
The researchers posit that the pesticide affects these birds by killing off their bug food supply. Concerns have been raised about neonicotinoids’ affect on bees since the chemical first emerged on the pesticide scene in the 1990s. What makes them popular is the fact that they’re supposed to only harm insect pests keen to munch on plant leaves.
How do insect pesticides work?
In insects, the pesticide binds to specific receptors in the nervous system, ultimately killing the insect. Because the chemical has a lower binding affinity to the same type of receptor in mammals, birds, and other larger animals, it’s also supposed to be less toxic and thus less dangerous to those species.
What are the negative effects of pesticides on birds?
Sublethal Effects In doses that do not kill, pesticides cause a myriad of adverse effects on the health of birds. These can include a reduction in the amount of food consumed, loss of weight, changes in physical activity, and a decrease in the production, fertility, or hatchability of eggs.
How can farmers protect birds from pesticides and herbicides?
Farmers could reduce birds’ exposure to these pesticides and herbicides by coming up with better ways to bury seeds, and remove seeds that spill during planting. They could also apply pesticides to plants only after an insect outbreak occurs – but again, since insects are a source of food for many birds, this option may not be best.
Are there pesticides in the air?
Many pesticides have been detected in air at more than half the sites sampled nationwide. Herbicides are designed to kill plants, so it is not surprising that they can injure or kill desirable species if they are applied directly to such plants, or if they drift or volatilise onto them.
What are pesticides doing to birds?
When it Comes to Pesticides, Birds are Sitting Ducks. The word pesticide is a catch-all term for chemicals that kill or control anything that humans have deemed to be a pest. Such chemicals can be grouped according to the kind of organism targeted, such as insecticide (insect), herbicide (weed), fungicide (fungus), or rodenticide (rodent).
How many pesticides are there in a bird nest?
“We found a total of 36 different pesticides in 95 mesh nests,” Geert Gommers, a pesticide expert, said in a statement released with the results. An analysis of the birds’ nests revealed traces of fungicides, herbicides, insecticides and biocides.
How do insecticides affect the environment?
Soil and groundwater can be contaminated by insecticides used to treat outdoor pests. Wild animals, including birds, may also be harmed or killed by ingesting toxic insecticides.
What are pesticides and why are they bad?
Pesticides are found as common contaminants in soil, air, and water, and on non-target vegetation in our urban landscapes. Once there, they can harm plants and animals ranging from beneficial soil microorganisms and insects, non-target plants, fish, birds, and other wildlife.
How do pesticides harm fish?
When pesticides contaminate water they can be harmful to the fish that live there. Insecticides can be particularly toxic to fish.