- How many vertebrae does a Simosuchus have?
- What type of animal is Simosuchus?
- What is the postcranial skeleton of Simosuchus like?
- Why is Simosuchus called a pug nose crocodile?
- Did Simosuchus have a fossorial lifestyle?
- Are Simosuchus and other notosuchians related?
- Where is the occipital condyle on a Simosuchus?
- How is Simosuchus related to other mammals?
- What is the scientific name for a pug-nosed crocodile?
- What is the spinal column of a reptile called?
- What did Simosuchus clarki look like?
- How many vertebrae are in the tail of Simosuchus?
- What is the type species of Simosuchus?
- Is Simosuchus a crocodile?
- What are the components of the postcranial skeleton?
- Was Simosuchus a herbivore or carnivore?
- Is Simosuchus and Chimaerasuchus the same?
- How did Simosuchus arrive in Madagascar?
- How did the crocodile lizard get its name?
- What is the scientific name for a crocodile called?
- What is the shape of the snout of Simosuchus?
- Are mammals more closely related to reptiles or amphibians?
- What is the occipital condyle in a reptile?
How many vertebrae does a Simosuchus have?
Most of the spinal column of Simosuchus is known. There are eight cervical vertebrae in the neck, at least fifteen dorsal vertebrae in the back, two sacral vertebrae at the hip, and no more than twenty caudal vertebrae in the tail. The number of vertebrae in the tail is less than that of most crocodyliforms, giving Simosuchus a very short tail.
What type of animal is Simosuchus?
Simosuchus (meaning “pug-nosed crocodile” in Greek, referring to the animal’s blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about 1 metre (3. 3 ft) in length. The type species is S.
What is the postcranial skeleton of Simosuchus like?
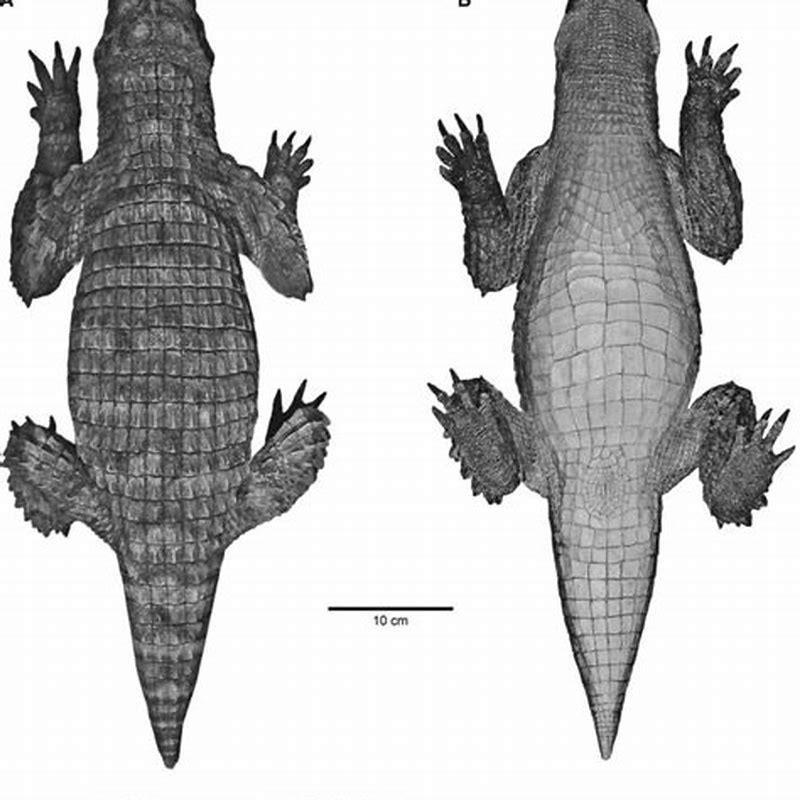
In most respects, the postcranial skeleton of Simosuchus resembles that of other terrestrial crocodyliforms. There are several differences, however, that have been used to distinguish it from related forms. The scapula is broad and tripartite. On its surface, there is a laterally directed prominence.
Why is Simosuchus called a pug nose crocodile?
In contrast to most other crocodyliforms, which have long, low skulls, Simosuchus has a distinctively short snout. The snout resembles that of a pug, giving the genus its name, which means “pug-nosed crocodile” in Greek.
Did Simosuchus have a fossorial lifestyle?
A fossorial, or burrowing lifestyle, for Simosuchus has recently been proposed but is not widely agreed upon. Evidence for burrowing includes the robust limbs and short snout, which appears shovel-like. There are also areas on the skull that may have attached to strong neck muscles that would have been well suited for burrowing.
Are Simosuchus and other notosuchians related?
The phylogenetic analysis of Carvalho et al. (2004), based on different character values than previous studies, produced a very different relationship among Simosuchus and other notosuchians. Simosuchus, along with Uruguaysuchus and Comahuesuchus, were placed outside Notosuchia.
Where is the occipital condyle on a Simosuchus?
At the back of the skull, the occipital condyle (which articulates with the neck vertebrae) is downturned. 45 autapomorphies, or features unique to Simosuchus, can be found in the skull alone. In most respects, the postcranial skeleton of Simosuchus resembles that of other terrestrial crocodyliforms.
How is Simosuchus related to other mammals?
Simosuchus was first considered to be a basal member of the clade Notosuchia, and was often considered to be closely related to Uruguaysuchus from the Late Cretaceous of Uruguay and Malawisuchus from the Early Cretaceous of Malawi.
What is the scientific name for a pug-nosed crocodile?
Simosuchus (meaning “pug-nosed crocodile” in Greek, referring to the animal’s blunt snout) is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorphs from the Late Cretaceous of Madagascar. It is named for its unusually short skull. Fully grown individuals were about 0.75 metres (2.5 ft) in length.
What is the spinal column of a reptile called?
Except in the snakes and legless lizards, where but two regions are recognized, the caudal and precaudal, the spinal column of reptiles is divisible into cervical, dorsal, sacral, and caudal regions, and sometimes lumbar also, as in mammals.
What did Simosuchus clarki look like?
The first specimen of Simosuchus clarki, which served as the basis for its initial description in 2000, included a complete skull and lower jaw, the front of the postcranial skeleton, and parts of the posterior postcranial skeleton. Five more specimens were later described, representing the majority of the skeleton.
How many vertebrae are in the tail of Simosuchus?
There are eight cervical vertebrae in the neck, at least fifteen dorsal vertebrae in the back, two sacral vertebrae at the hip, and no more than twenty caudal vertebrae in the tail. The number of vertebrae in the tail is less than that of most crocodyliforms, giving Simosuchus a very short tail.
What is the type species of Simosuchus?
The type species is Simosuchus clarki, found from the Maevarano Formation in Mahajanga Province, although some fossils have been found in India. The teeth of S. clarki were shaped like maple leaves, which coupled with its short and deep snout suggests it was not a carnivore like most other crocodylomorphs.
Is Simosuchus a crocodile?
Over the next decade, expeditions to Madagascar recovered more skulls and skeletons, now representing nearly every bone of Simosuchus. A reconstruction of this uncommonly complete fossil reptile and an interpretation of its place in the crocodile evolutionary tree became the subject of the new volume.
What are the components of the postcranial skeleton?
The postcranial skeleton includes all the bones and cartilages caudal to the head skeleton; it is subdivided into axial components (the vertebral column, ribs, and sternebrae, which are “on” the midline) and appendicular components (the forelimbs, hindlimbs, and pectoral and pelvic girdles, which are “off” the midline).
Was Simosuchus a herbivore or carnivore?
Simosuchus, like other notosuchians, was fully terrestrial. Features of the skull such as the clove-shaped teeth strongly suggest terrestrial herbivory. The short tail would have had little use in swimming. The osteoderm shield was inflexible, restricting lateral movement in Simosuchus as a possible adaptation to an entirely terrestrial lifestyle.
Is Simosuchus and Chimaerasuchus the same?
Simosuchus was found to be the sister taxon of the Chinese genus Chimaerasuchus in the family Chimaerasuchidae. Like Simosuchus, Chimaerasuchus has a short snout and was probably herbivorous. Both genera were placed outside Notosuchia in the larger clade Gondwanasuchia.
How did Simosuchus arrive in Madagascar?
It is unknown how Simosuchus arrived in Madagascar. A similar crocodyliform, Araripesuchus tsangatsangana, is also known from the Maevarano Formation, but its relation to Simosuchus is unclear. It has been classified as both a notosuchian and a basal neosuchian in various phylogenetic analyses.
How did the crocodile lizard get its name?
Its name is derived from the bony scales running along its back and tail, giving it a crocodile-like appearance though it is much smaller than actual crocodiles, only reaching 16 – 18 inches (40-46 cm) in length. The crocodile lizard is semi-aquatic, living in shallow waters or on overhanging branches and leaves.
What is the scientific name for a crocodile called?
Lacerta gangetica was the scientific name proposed by Johann Friedrich Gmelin in 1789. Gmelin followed Carl Linnaeus who proposed Lacerta in 1758 to include other crocodiles and various lizards known at the time. The gharial was placed in the genus Crocodilus by subsequent naturalists: C. gavial by Pierre Joseph Bonnaterre in 1789.
What is the shape of the snout of Simosuchus?
Simosuchus had a distinctively short snout. The snout resembles that of a pug, giving the genus its name, which means “pug-nosed crocodile” in Greek. The shape of skulls differs considerably between specimens, with variation in ornamentation and bony projections. This difference may be an indication of sexual dimorphism in the genus.
Are mammals more closely related to reptiles or amphibians?
Mammals are very slightly more closely related to birds (and other reptiles) than either reptiles or mammals are to amphibians. Why do amphibians not have scales when they are closer to fish than reptiles? Why do amphibians not have scales when they are closer to fish than reptiles?
What is the occipital condyle in a reptile?
The occipital condyle is the structure on the back of the skull that allows it to articulate with the first neck vertebra. Most reptiles have only one occipital condyle, while mammals have two. Also, what type of skull Do reptiles have?