- What is the unit of measurement for equine measurements?
- What is the normal blood sugar for a horse?
- What is the total protein range of a horse?
- What does it mean when a horse has yellow blood cells?
- What is a gamma globulin test for horses?
- What causes protein levels to decrease in a horse’s blood?
- What is an IgG test on a horse?
- How to tell if a horse has EIA antibodies?
- Why is protein bad for horses?
- Can goat antibodies cross react with horse IgG (T)?
- What is a normal serum IgG level in a horse?
- What does IgG mean on a foal?
- How to measure colostral IgG in horses?
- How long does it take for antibodies to show up in horses?
- How do I know if my horse is immune to EAV?
- What does a low total protein and albumin level mean?
- What is the IgG level of a foal?
- What is the best antibody for horse allergies?
- Which tissue targets are targeted in antibody assessments for equine infection?
- Are there any antibodies available to investigate infectious CNS diseases in horses?
- Can equine IgG (T) antibodies cross react with other equine immunoglobulin classes?
- What is a normal colostrum level for a foal?
- What is normal IgG in foals?
- How do you measure IgG in colostrum?
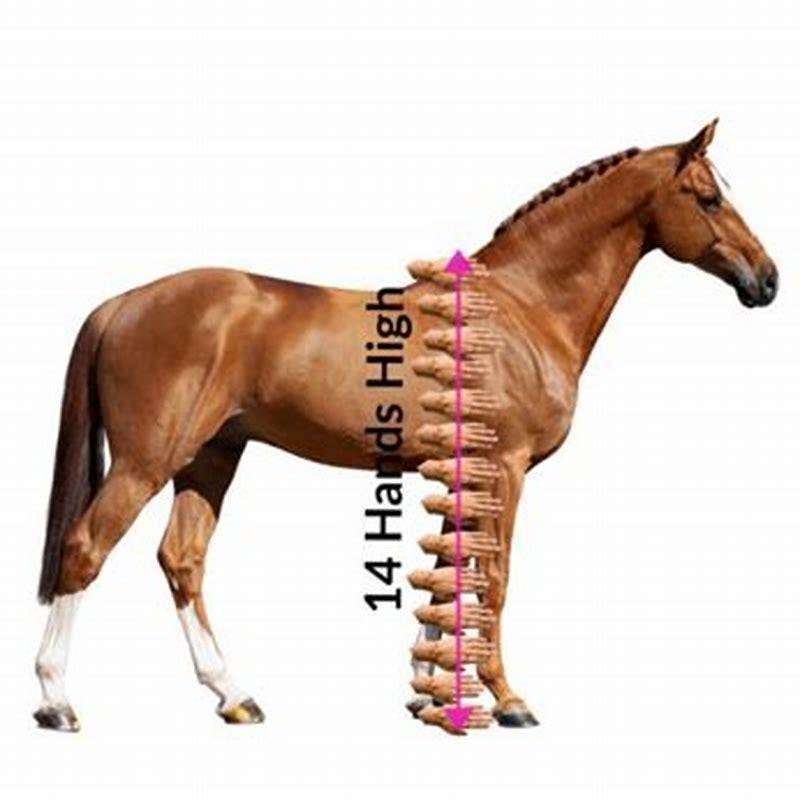
What is the unit of measurement for equine measurements?
Equines are measured in units. Which unit of measure is used depends on the association doing the registration. Some registries use inches to determine size, since it is easier than trying to convert to hands. A hand is four inches. The story behind this unit of measurement is that a kind went to measure his favorite horse.
What is the normal blood sugar for a horse?
EQUINE CLINICAL PATHOLOGY NORMAL VALUES Clinical Chemistry Normal Values for Horses ALB 2.5 – 4.2 g/dL ALKP 109 – 315 U/L ALT 3 – 25 U/L AMYL < 30 U/L AST 205 – 555 U/L BUN 8 -27 mg/dL
What is the total protein range of a horse?
Age Total Protein Range (g/l) Albumin Range (g/l) Globulin Range (g/l) Adult Non-Thoroughbred Horses 53-73 29-41 18-38 Neonatal Thoroughbred Foals (24-48hrs ol … 41-66 25-35 15-36 Older Thoroughbred Foals (approx. 3 week … 42-66 26-37 15-33 Yearling Thoroughbred Horses 52-64 31-38 18-29 3 more rows
What does it mean when a horse has yellow blood cells?
Causes the yellowing of tissues called “jaundice”. It is used as a measure of liver function. Elevated levels indicate liver disease, but can also be increased if the horse is not eating, or if a disease process is destroying red blood cells in the body.
What is a gamma globulin test for horses?
Veterinarians have developed tests to measure the amount of gamma globulins within the foal’s bloodstream to estimate if an “adequate” quantity of immunoglobulins has been ingested and absorbed by the foal. These tests measure the gamma globulin concentrations within the bloodstream.
What causes protein levels to decrease in a horse’s blood?
Decreased levels occur with passive transfer failure in foals, severe protein loss. Total protein, measures protein in the blood; can indicate dehydration if elevated. Decreases with kidney & GI disease, liver failure & starvation
What is an IgG test on a horse?
An IgG Test or a Gamma E Check Test involves taking a blood sample from the foal at 12-16 hours of age. This is used to determine if the foal has received and absorbed enough of the important antibodies that are passed through the mare’s colostrum.
How to tell if a horse has EIA antibodies?
There are multiple tests to detect if a horse has EIA antibodies, but the Coggins test is the most popular and well known among horse industry professionals. To perform a Coggins test, a licensed veterinarian must draw blood from your horse and send it to an accredited lab for analysis.
Why is protein bad for horses?
Proteins are difficult to digest in horses, which is a good thing. But overtaking it can cause the gluconeogenesis process, which the horse undertakes when breaking down protein, is a fluctuation in the horse cortisol levels, making it feel fatigued.
Can goat antibodies cross react with horse IgG (T)?
Goat anti Horse IgG (T) antibody recognizes equine IgG (T). No cross-reactivity with other equine immunoglobulin classes is seen in immuno-electrophoresis. Goat anti Horse IgG (T) antibody may cross react with IgG from other species.
What is a normal serum IgG level in a horse?
Serum samples should be taken from foals on the second day of life when IgG levels should ideally be >8 g/l. Levels <4 g/l suggest failure and 4-8 g/l suggest partial failure of colostral immunity, and prophylactic measures may be indicated, dependent on the result and clinical setting/risk factors.
What does IgG mean on a foal?
We will start this story on foal IgG with a more general discussion of the immunoproteins, or “Igs,” in an effort to give a better understanding of what these terms stand for and the importance of what they do. The term IgG stands for “immunoglobulin” type G, sometimes referred to as gamma globulin G.
How to measure colostral IgG in horses?
Colostral IgG is measured semi-quantitatively immediately after parturition, using a refractometer (Colostrometer). If readings suggest an IgG level of less than 45g/l, the foal should be considered for donor colostrum supplementation.
How long does it take for antibodies to show up in horses?
Detectable antibodies are usually present in the blood 7-14 days after infection and remain present for the rest of the horse’s life. Diagnosis should be by means of the Coggins test, which is currently the only test recognised officially for the purpose of international movement of horses.
How do I know if my horse is immune to EAV?
Vaccination should protect a horse against the disease for at least a year. A blood test can confirm whether a horse has antibodies to the virus and the level of its immunity to this infection. This test cannot differentiate between a horse that is positive for antibodies to EAV as a result of vaccination or from natural exposure to the virus.
What does a low total protein and albumin level mean?
Plasma Total Protein & Albumin. Protein levels in blood are an important indicator of health. High levels can indicate dehydration. Low levels can indicate loss of protein from the blood, usually into the intestinal or urinary tract. The bulk of Total Protein is made up of several important proteins, globulin and albumin,…
What is the IgG level of a foal?
Measure the foal’s Ig (IgG, specifically) levels between 18 and 24 hours of life to ensure sufficient passive transfer has been achieved. Ideally, IgG levels exceed 8 grams/liter.
What is the best antibody for horse allergies?
Horseradish peroxidase conjugated Goat anti Horse IgGT antibody used for the determination of allergen specific antibody titre in horse serum by ELISA. Healthy horses have allergen-specific serum antibodies.
Which tissue targets are targeted in antibody assessments for equine infection?
Initial evaluation of antibody binding was tested on non-infected equine lymph node and spleen for lymphocytic targets, liver and thymus for tissue macrophage targets, and brain for microglia, astrocytes, and neurons. Tissue processing
Are there any antibodies available to investigate infectious CNS diseases in horses?
This study identified a set of antibodies for investigating the immunopathology of infectious CNS diseases in horses. Multiple commercially available staining reagents and antibodies derived from antigens of various species for manual immunohistochemistry (IHC) were screened.
Can equine IgG (T) antibodies cross react with other equine immunoglobulin classes?
No cross-reactivity with other equine immunoglobulin classes is seen in immuno-electrophoresis. Goat anti Horse IgG (T) antibody may cross react with IgG from other species. Antisera to equine IgG (T) were raised by repeated immunisation of goat with highly purified antigen.
What is a normal colostrum level for a foal?
If readings suggest an IgG level of less than 45g/l, the foal should be considered for donor colostrum supplementation.
What is normal IgG in foals?
– Kentucky Equine Research Immunity of Foals: What Is Normal IgG? Foals are born with an intact, though low-functioning, immune system. Because there is no transfer of immunoglobulins, including immunoglobulin G (IgG), from mares to their fetuses in the uterus, foals depend on antibodies they acquire from colostrum to fend off pathogenic assaults.
How do you measure IgG in colostrum?
Measuring IgG in colostrum can be used to predict failure of passive transfer in the foal. Colostral IgG is measured semi-quantitatively immediately after parturition, using a refractometer (Colostrometer). If readings suggest an IgG level of less than 45g/l, the foal should be considered for donor colostrum supplementation.