- Is the Titanoboa venomous?
- What is the physical description of a Titanoboa?
- Are today’s largest snakes as big as Titanoboa?
- Why was the Titanoboa so dangerous?
- What can we learn from a snake skull found in Cerrejón?
- Can a Titanoboa climb trees?
- How big was Titanoboa the Snake?
- Did the Titanoboa snake really overheat?
- Is the Titanoboa dangerous?
- Are reptiles a monophyletic group?
- Where can I find the text of the 1920 article serpents?
- Why do snakes have more joints in their heads than lizards?
- What is the skeleton of a snake?
- Where can I find a bibliography for the article serpents?
- Can snakes climb trees?
- Can a Titanoboa eat a turtle?
- Why was the Titanoboa more dangerous while in water?
- Why did Titanoboa go extinct?
- What is the biggest Titanoboa?
- Are frogs amphibians or mammals?
- What is a monophyletic group in biology?
- Do all reptiles have a kinetic skull?
- Why do snakes have bones in their body?
- What kind of skull does a lizard have?
- What bones are in a snake’s skeleton?
- Why are they called red snakes in the Bible?
Is the Titanoboa venomous?
The Titanoboa was not venomous. It, therefore, killed its prey physically by either constriction or blocking the windpipe and not by the use of venom. Its diet constituted of other reptiles of smaller sizes, birds, and small crocodiles.
What is the physical description of a Titanoboa?
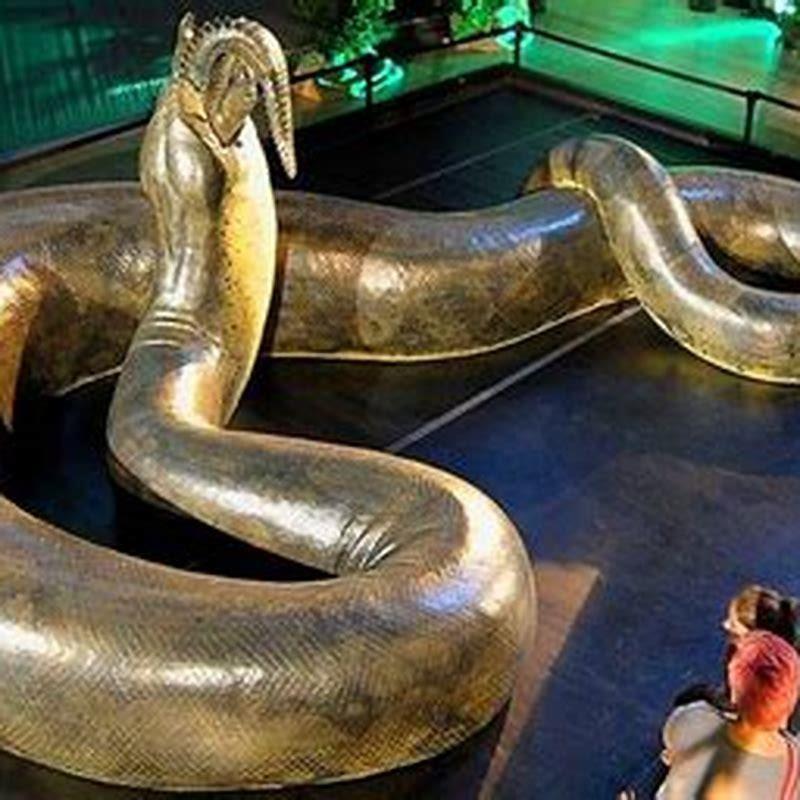
Physical Description. Titanoboa was a large snake that measured around 50 feet. Its weight was between 2300 and 2500 pounds. It had a diameter of about 3 feet at its thickest. This size is almost twice larger than the modern day’s largest snake.
Are today’s largest snakes as big as Titanoboa?
Today’s largest snakes are not as big as Titanoboa. Considering that this Paleocene reptile is systematized as a member of the Boinae subfamily, a comparison with its modern-world relative: anaconda, would be to the point.
Why was the Titanoboa so dangerous?
The large size would have made it difficult for the Titanoboa to climb trees. The snake may have been more dangerous while in water since its weight was helped by the buoyancy of water. The Titanoboa, just like many other modern reptiles, had mating seasons.
What can we learn from a snake skull found in Cerrejón?
The snake skull embraced by the Cerrejón shale mudstone was a piece of Titanoboa that Bloch, Head and their colleagues had been hoping to find for years. “It offers a whole new set of characteristics,” Bloch said. The skull will enhance researchers’ ability to compare Titanoboa to other snakes and figure out where it sits on the evolutionary tree.
Can a Titanoboa climb trees?
Due to its large size, the Titanoboa spent most of its terrestrial times slithering around trees. The large size would have made it difficult for the Titanoboa to climb trees. The snake may have been more dangerous while in water since its weight was helped by the buoyancy of water.
How big was Titanoboa the Snake?
It was 50 feet long the biggest snake in the world, probably longer than the T.Rex at times. Titanoboa was one of the largest land animals of it’s time, so it needed a lot of food to keep healthy. However it did not eat that often.
Did the Titanoboa snake really overheat?
In another critique, Stanford’s Mark Denny, a specialist in biomechanics, says the Titanoboa researchers have it backward: The snake was so large and was producing so much metabolic heat that the ambient temperature must have been four to six degrees cooler than the team’s estimate, or the snake would have overheated.
Is the Titanoboa dangerous?
However, the Titanoboa’s venomous bite is so potent that it is known to paralyze far larger creatures. Titanoboa has developed a strange coexistence with other creatures of the Island’s caves.
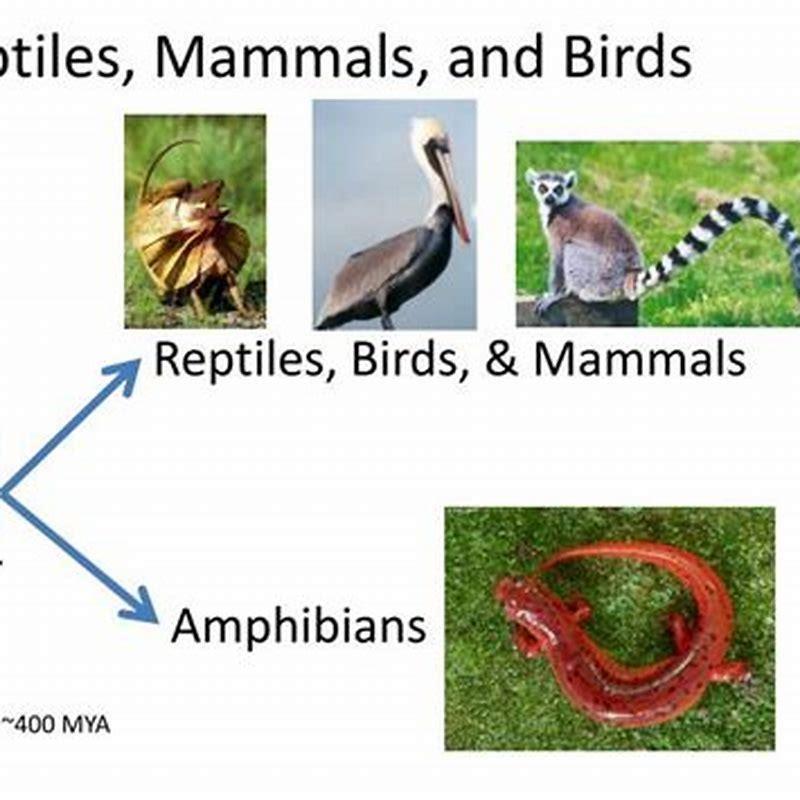
Are reptiles a monophyletic group?
The term Reptiles as used in popular language does not represent a monophyletic group. When using the term Reptiles, one is typically thinking of turtles, snakes and lizards but excluding birds and mammals (and a few other things not worth mentioning).
Where can I find the text of the 1920 article serpents?
Wikisource has the text of the 1920 Encyclopedia Americana article Serpents. “Bibliography for “Serpentes ” “. Biodiversity Heritage Library. “Serpentes”. Integrated Taxonomic Information System. “US Snakes”. eNature. Archived from the original on 15 March 2008. “Snakes of the Indian Subcontinent”. Naturemagics Kerala Photo Gallery.
Why do snakes have more joints in their heads than lizards?
Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads with their highly mobile jaws.
What is the skeleton of a snake?
The skeletons of snakes are radically different from those of most other reptiles (as compared with the turtle here, for example), consisting almost entirely of an extended ribcage. The skeleton of most snakes consists solely of the skull, hyoid, vertebral column, and ribs, though henophidian snakes retain vestiges of the pelvis and rear limbs.
Where can I find a bibliography for the article serpents?
Look up snake in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Wikisource has the text of the 1920 Encyclopedia Americana article Serpents. “Bibliography for “Serpentes ” “.
Can snakes climb trees?
Snakes and lizards are great at climbing anything they can slither or climb up…even monitor lizards can climb trees and they’re quite big Yes, almost any snake that I can think of, with the possible exception of sea snakes, has the ability to climb trees. However, while snakes like the anaconda have the ability, they almost never do.
Can a Titanoboa eat a turtle?
The crocs and the turtles undoubtedly ate fish, but Titanoboa was at the top of the food chain. It could eat fish, but it could also eat the crocs and turtles. “Some snakes—especially anacondas—can and do eat crocodilians,” Head said.
Why was the Titanoboa more dangerous while in water?
The snake may have been more dangerous while in water since its weight was helped by the buoyancy of water. The Titanoboa, just like many other modern reptiles, had mating seasons.
Why did Titanoboa go extinct?
Although no one knows the exact reason why Titanoboa went extinct, two theories have been put forward. Climate change contributed to the disappearance and extinction of most of Titanoboa. The declining global temperatures favored the emergence of smaller snakes.
What is the biggest Titanoboa?
Twice as Long as Today’s Longest Snakes Titanoboa was only twice as long and four times as heavy as the modern-day giant anaconda, the largest specimens of which measure 25 feet from head to tail and weigh 500 pounds. Compared to most modern snakes, however, titanoboa was a true behemoth.
Are frogs amphibians or mammals?
Any animal (eg, crocodile, hippo, frog and capybara) that can live in water and on land may be described as being AMPHIBIOUS, but only frogs, toads, caecilians, newts and salamanders are AMPHIBIANS.
What is a monophyletic group in biology?
Monophyletic taxon : A group composed of a collection of organisms, including the most recent common ancestor of all those organisms and all the descendants of that most recent common ancestor. A monophyletic taxon is also called a clade. Examples : Mammalia, Aves (birds), angiosperms, insects, etc. Do reptiles form a monophyletic group?
Do all reptiles have a kinetic skull?
All reptiles of the super order Lepidosauria (lizards, snakes, and tuatara) have kinetic skulls, but they differ from the dinosaurs in that the joint on the floor of the skull occurs at the juncture of basisphenoid and pterygoid bones in lepidosaurians. The skulls of the lepidosaurians became increasingly kinetic as new groups evolved.
Why do snakes have bones in their body?
In the case of the snake, its skeleton consists of all the individual snake bones. The bones give a place for all the muscles to attach and protect internal organs. When combined with the cartilage that keeps them all together, the bones become a skeleton that gives shape, or structure, to the snake’s body.
What kind of skull does a lizard have?
All reptiles of the super order Lepidosauria (lizards, snakes, and tuatara) have kinetic skulls, but they differ from the dinosaurs in that the joint on the floor of the skull occurs at the juncture of basisphenoid and pterygoid bones in lepidosaurians.
What bones are in a snake’s skeleton?
A snake’s skeleton is made up primarily of vertebrae, rib bones, jawbones, and a skull. Some species, like boas and pythons, also have a hip bone.
Why are they called red snakes in the Bible?
The word appears to denote a particular kind of serpent, as in the following verse. Some think that they were so called because of the bright fiery red upon their heads; others because of the blazing sunbeams on their scales; and others because of their inflammatory and poisonous bite. Venomous snakes are said to abound still in the Arabah.